- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
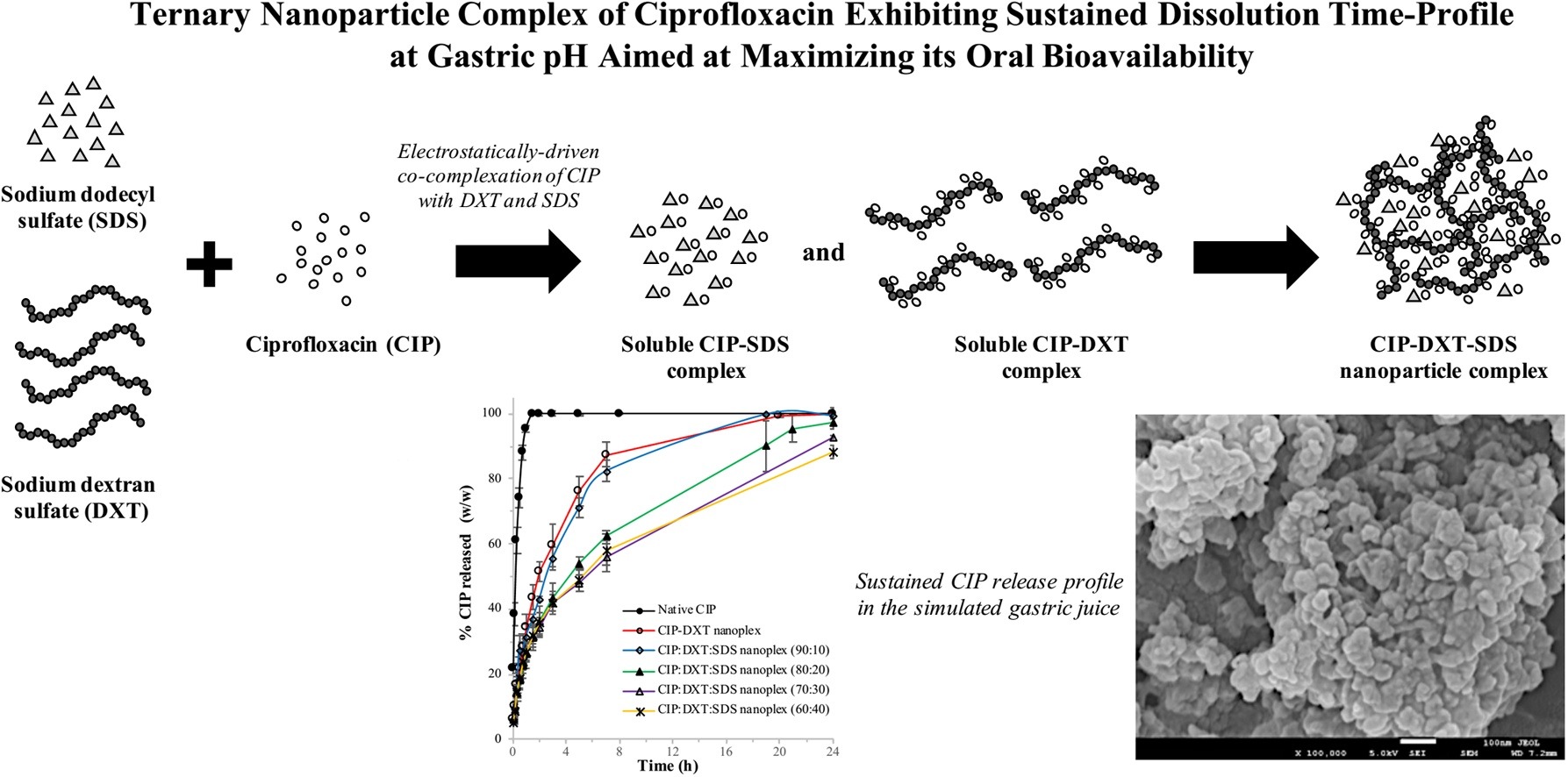
• Ternary nanoplexes form by electrostatic co-complexation of CIP with DXT and SDS.
• The ternary nanoplexes contain amorphous CIP-DXT and crystalline CIP-SDS complexes.
• The CIP-DXT and CIP-SDS compositions vary with the ratio of DXT to SDS.
• CIP-DXT-SDS has better sustained release at gastric pH than CIP-DXT-SDS.
• CIP-DXT-SDS exhibits similar dissolution as a CIP gastroretentive formulation.
Poor bioavailability of the broad spectrum antibiotic ciprofloxacin (CIP) is caused by its narrow absorption window in the stomach. With the aim of prolonging the gastric residence time of CIP, we prepared a ternary nanoparticle complex (nanoplex) of CIP by co-complexation with polyanions (sodium dextran sulfate (DXT)) and an anionic amphiphile (sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)). We investigated the effect of the charge ratio of DXT to SDS on the size, zeta potential, CIP payload, and CIP utilization rate of the CIP-DXT-SDS nanoplex and its dissolution characteristics in simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, and differential scanning calorimetry analyses showed that the ternary nanoplex was made up of amorphous CIP-DXT and crystalline CIP-SDS complexes. The size of the CIP-DXT-SDS nanoplex prepared at a > 90% CIP utilization rate was 110–290 nm and it had a zeta potential of −16–39 mV, and CIP payload of 47–62%, depending on the charge ratio. At gastric pH, the CIP-DXT-SDS nanoplex prepared with a DXT:SDS charge ratio lower than 80:20 exhibited prolonged CIP release (60% dissolution after 8 h) compared with native CIP (100% dissolution after 1 h) and a binary CIP-DXT nanoplex (80% dissolution after 5 h), which was attributed to its lower solubility. The sustained release characteristics of the CIP-DXT-SDS nanoplex were comparable to those of existing CIP gastroretentive formulations.