- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
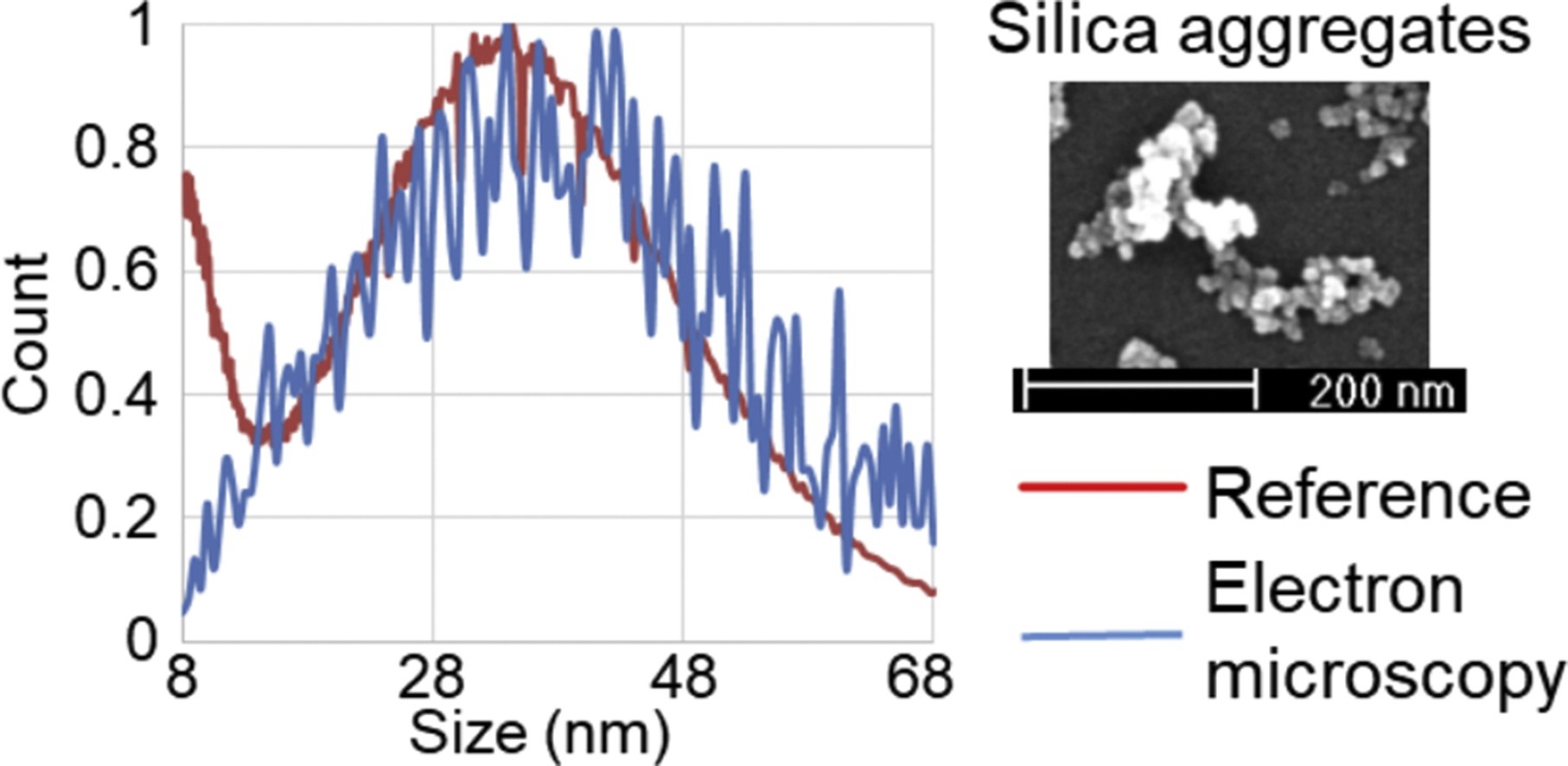
• A new approach for the measurement of nanoparticle aggregates using electron microscopy.
• Determination of a sample preparation protocol that did not introduce agglomeration.
• Comparison of measurements between electron microscopy and reference methods.
• Skewing artefact introduced by sample preparation was refined using mathematical solution.
• Mathematical solution differed for gold and silica nanoparticles.
Electron microscopy (EM) is widely used for nanoparticle (NP) sizing. Following an initial assessment of two sample preparation protocols described in the current literature as "unperturbed", we found that neither could accurately measure the size of NPs featuring a broad size distribution, e.g., aggregates. Because many real-world NP samples consist of aggregates, this finding was of considerable concern. The data showed that the protocols introduced errors into the measurement by either inducing agglomeration artefacts or providing a skewed size distribution towards small particles (skewing artefact). The focus of this work was to develop and apply a mathematical refinement to correct the skewing artefact. This refinement provided a much improved agreement between EM and a reference methodology, when applied to the measurement of synthetic amorphous silica NPs. Further investigation, highlighted the influence of NP chemistry on the refinement. This study emphasised the urgent need for greater and more detailed consideration regarding the sample preparation of NP aggregates to routinely achieve accurate measurements by EM. This study also provided a novel refinement solution applicable to the size characterisation of silica and citrate-coated gold NPs featuring broad size distributions. With further research, this approach could be extended to other NP types.