- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
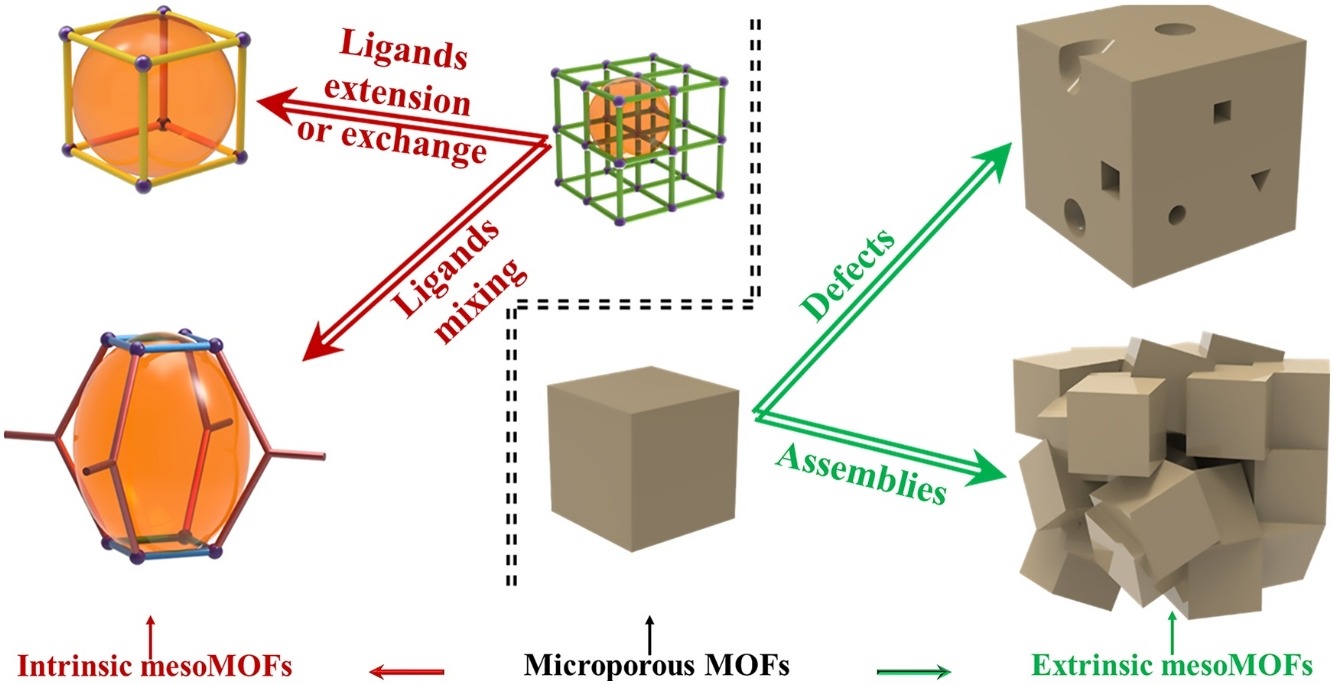
• Recent advances in mesoporous metal-organic frameworks (mesoMOFs) reported since 2013 are summarized.
• MesoMOFs are termed intrinsic or extrinsic based on the structure formation process.
• Both synthesis strategies and specific applications are reviewed.
• Personal viewpoints on future research directions and challenges are provided.
Highly porous and crystalline metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted widespread attention and have significant potential for applications in many fields. However, the microporous structure of most existing MOFs has been found to be disadvantageous with regard to mass transfer and the availability of active sites. Hence, the creation of mesopores in MOFs is of interest. This review focuses on recent advances in the study of mesoporous MOFs (mesoMOFs), as reported since 2013. These materials are classified as either intrinsic or extrinsic, according to the source of the mesopores. Intrinsic mesoMOFs are obtained from the extension, configuration design or mixing of ligands. In contrast, extrinsic mesoMOFs are synthesized by modulating the growth of crystals to introduce larger pores derived from defects and assemblies into the final product. This review also discusses specific applications of mesoMOFs, including catalysis, gas storage and adsorption, and liquid phase adsorption. Finally, the authors’ personal opinions concerning future research directions and challenges are provided.