- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
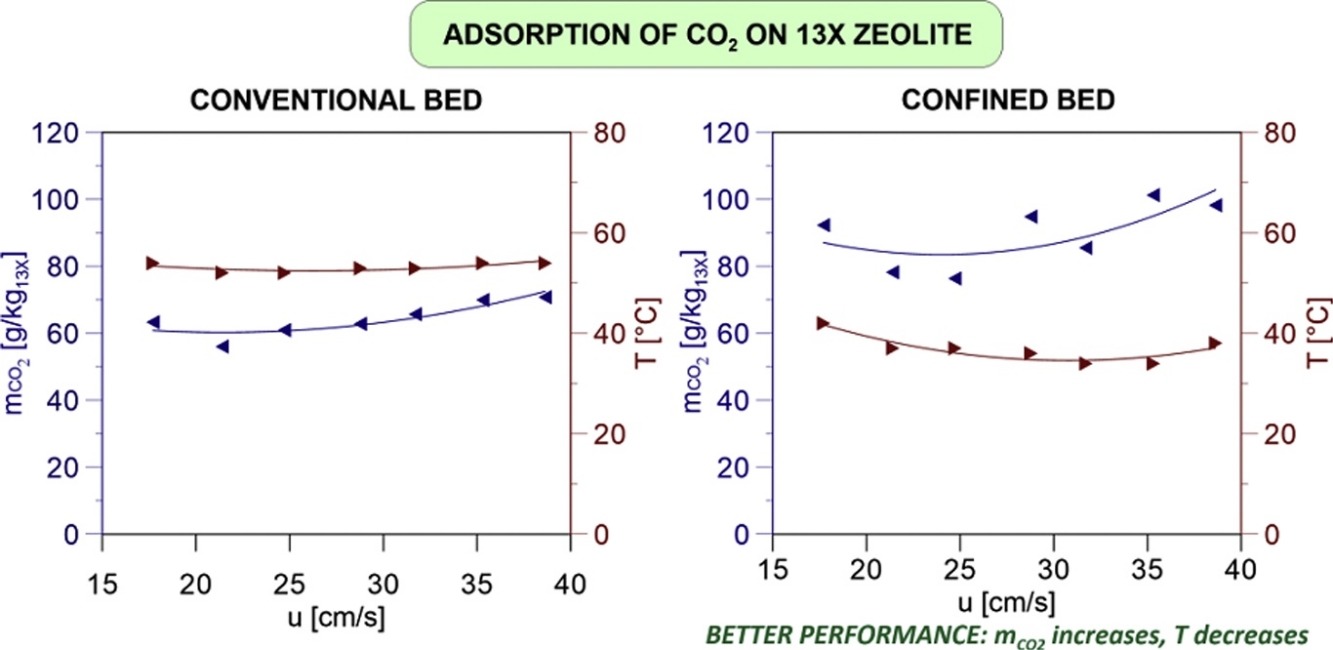
• Adsorption of CO2 on a confined fluidized bed of pelletized 13X zeolite is studied.
• A comparison is made with the results obtained from a conventional fluidized bed.
• Confined fluidization positively affects the efficiency of the adsorption process.
• The increase of breakthrough time and CO2 uptake is remarkable.
• The temperature increase associated with CO2 adsorption is more easily controlled.
CO2 adsorption is performed across a fluidized bed comprising a commercial pelletized 13X zeolite confined to the interstitial void network of a coarse glass sphere packed bed. Compared with traditional fixed bed adsorption, the packed fluidized system allows operation across a wide-range of gas velocities without a substantial increase in pressure drop. Additionally, with respect to conventional fluidization regimes, the technique adopted herein prevents the formation of bubbles in favour of enhancing the bed expansion ability. Furthermore, for a given mass of sorbent, the CO2 uptake capacity is observed to increase as a result of improved thermal conditions and in eliminating any by-pass effect at the gas–particle interface, which is associated to the suppression of bubbling.