- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
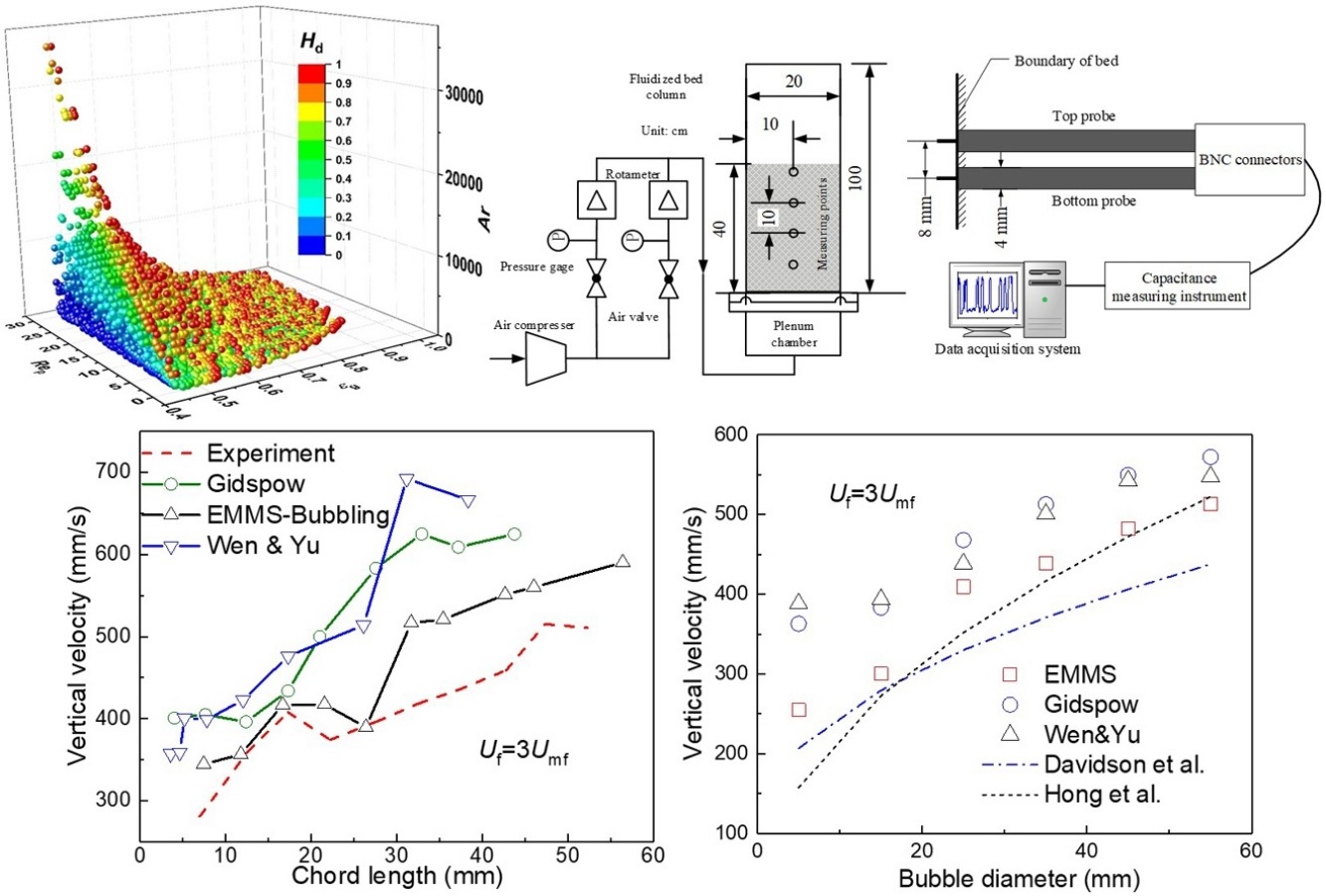
• Bubble behavior in a Q2D fluidized bed was simulated using EMMS model.
• A new correlation of the heterogeneous index in EMMS model was proposed.
• We extended the flood-fill algorithm to search bubbles from 2D to a Q2D bed.
• Results from empirical correlations, experiment and simulation are compared.
• EMMS approach has higher accuracy in predicting properties of bubbles.
Bubbles formed during chemical processes in fluidized beds govern the bed hydrodynamics and operational efficiency, thereby having a significant impact on their design and scale-up. In this study, a two-fluid model was used to simulate the bubble behavior in a quasi-two-dimensional fluidized bed within the bubble-based energy minimization multiscale (EMMS) approach. We performed experiments to verify the model and proposed a correlation of the heterogeneous index for various parameters to calculate the coefficient of drag for the bubble-based EMMS model. Moreover, the simulation results obtained from the homogeneous drag models and EMMS bubbling model were compared with experimental data and empirical correlations. The simulation results of the EMMS approach showed good agreement with the experimental data in the distribution of the vertical bubble velocity with chord length. Compared with the results from the homogeneous models, the distributions of vertical velocity and diameter of the bubbles predicted by the EMMS-bubbling model were in better agreement with empirical correlations. Moreover, the frequency distributions of bubble properties including bubble diameter, aspect ratio, and shape factor for different gas-inlet velocities were obtained.