- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
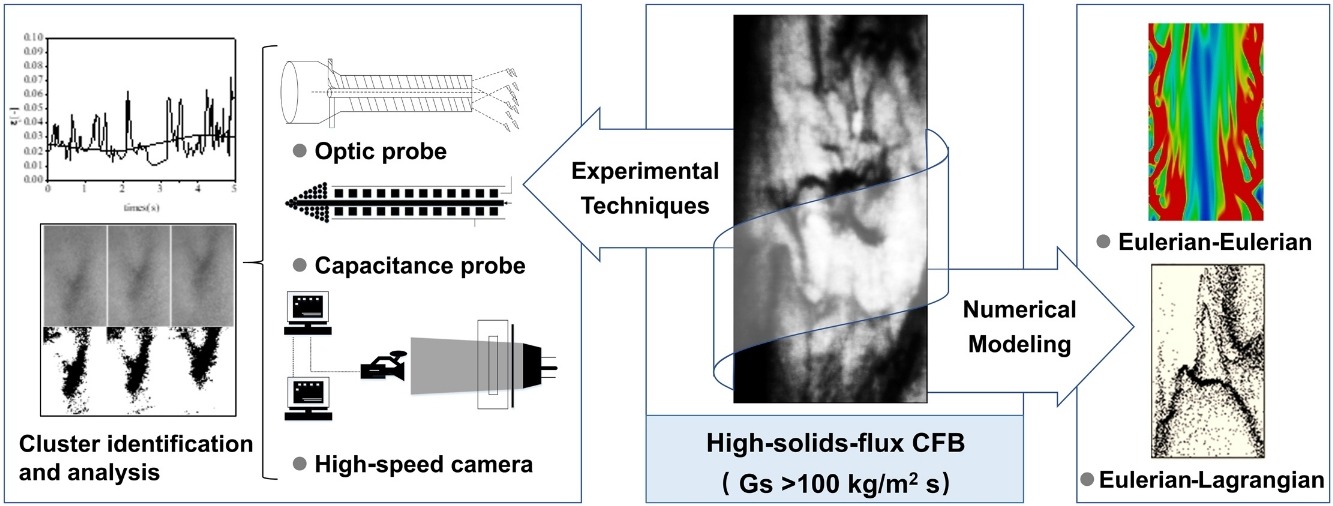
• Experimental and modeling researches on particle-clustering phenomenon in HFCFBs were reviewed.
• Experimental techniques and results of particle clustering in HFCFBs were discussed.
• Modeling of clustering with Eulerian–Eulerian and Eulerian–Lagrangian approaches were summarized.
Particle clustering is an important dynamic phenomenon in circulating-fluidized-bed (CFBs) systems, and has been suggested as a key contributing factor to the non-uniform hydrodynamics of CFBs. Studies show that particle clusters can be affected by solids flux, in terms of frequency, duration, and solids holdup. To understand the characteristics of particle clusters under high-solids-flux conditions, experimental and modeling studies in high-solids-flux gas–solids CFBs were reviewed and summarized. Optical and electrical measurements and imaging methods were used to monitor the particle-clustering phenomenon in CFBs. Particles were found to cluster in high-flux CFBs, and were characterized by a denser cluster-solids holdup and a shorter time fraction, which was different from the behavior in low-flux CFBs. Particle properties affected particle clustering in high-flux CFBs significantly. In modeling work, Eulerian–Eulerian and Eulerian–Lagrangian methods were used to study the particle-cluster characteristics. Good results can be obtained by using the Eulerian–Eulerian method to simulate the CFB system, especially the high-flux CFBs, and by considering the effects of particle clusters. The Eulerian–Lagrangian method is used to obtain detailed cluster characteristics. Because of limits in computing power, no obvious results exist to model particle clusters under high-solids-flux conditions. Because high-solids-flux conditions are used extensively in industrial applications, further experimental and numerical investigations on the clustering behavior in HF/DCFBs are required.