- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
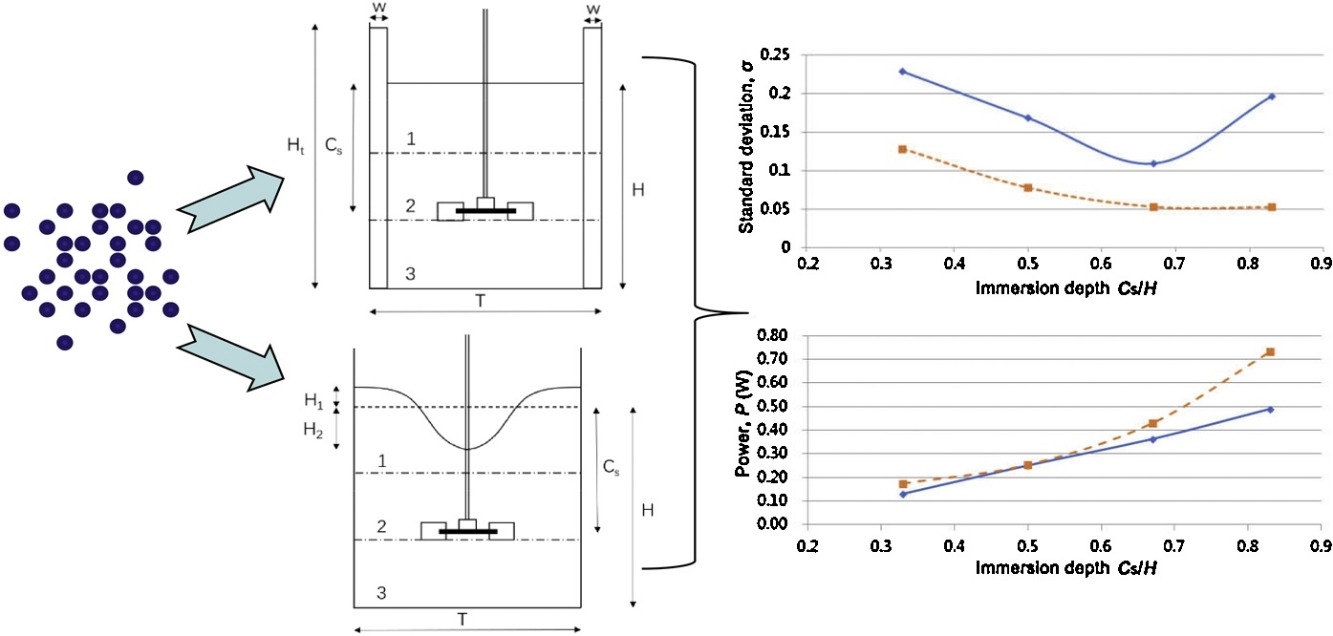
• Particle dispersion was analyzed during stirring in baffled and unbaffled tanks.
• Critical impeller speed was defined by particle distribution behavior.
• A dispersion index reasonably predicted particle drawdown in unbaffled tank.
• Baffles suppressed the surface vortex and more uniformly distributed particles.
• Baffled tanks increased power consumption.
The effects of surface vortex on the drawdown and dispersion of floating particles in stirred tanks were investigated. Particle distribution and power consumption were analyzed by experiments and numerical simulations in both baffled and unbaffled tanks agitated by a Rushton impeller. In unbaffled tanks, a non-aggregation rule was applied and the average dispersion index was found to serve as a reasonable prediction of the full drawdown of floating particles. The critical impeller speeds in an unbaffled tank were higher than those in a tank with vertical baffles. At each immersion depth in a baffled tank, particles distributed more uniformly and more power was consumed. Comparison of snapshots of the baffled and unbaffled tanks shows that the surface vortex increases the drawdown speed while it decreases the particle distribution uniformity and power consumption. Therefore, the use of baffles to suppress the surface vortex provides for a more uniform particle distribution in stirred tanks.