- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Torque and surface particle distributions were simulated with verified contact factors.
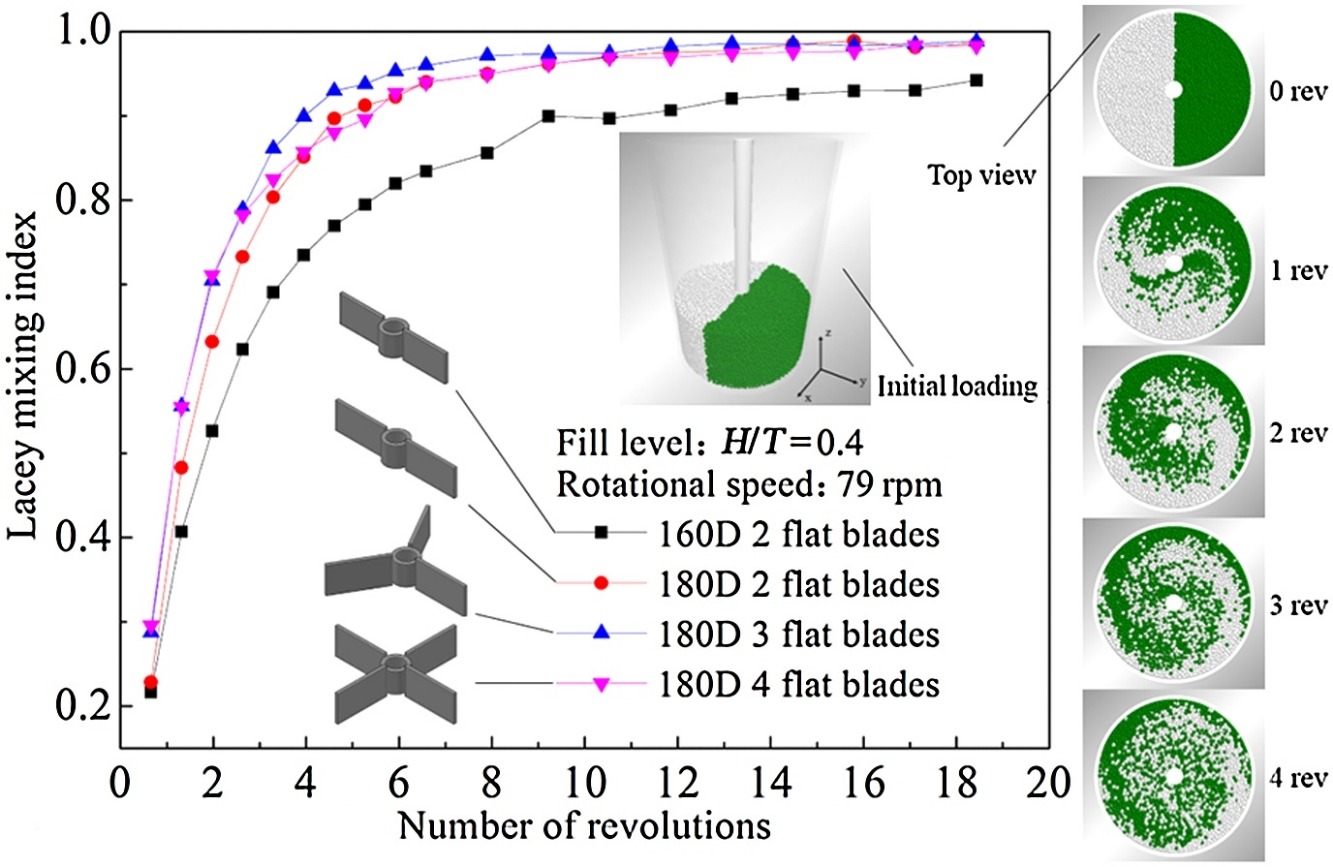
• The three-flat-blade mixer outperforms the two- or four-flat-blade mixer.
• Circumferential velocity most affects mixing performance for side-by-side loading.
We employed the discrete element method to study the effects of the impeller configuration (i.e., blade diameter, inclination angle, and blade number), rotational speed, and fill level on the flow and mixing of particles in a cylindrical mixer equipped with flat and inclined blades. The coefficient of rolling friction, coefficient of static friction, and coefficient of restitution were experimentally determined before the simulation, and simulation results of the torque and surface particle distribution were validated in experiments, particularly when using a true Young’s modulus in the discrete element method. The performance of the mixer was assessed using the Lacey mixing index. The input work per unit volume was used to represent the mixing efficiency. The circumferential velocity and axial diffusion coefficient of the particles were quantitatively analyzed to reveal the effect of particle flow on the mixing. It was found that the mixing performance and efficiency of a three-blade mixer are better than those of two- and four-blade mixers. For pitched blades, a three-flat-blade mixer has better mixing performance than a three-45°-blade own-pumping or a three-45°-blade up-pumping mixer, but the mixing efficiency of the three-45°-blade up-pumping mixer is the best among these three mixers. As the rotational speed increases, the mixing performance improves but the mixing efficiency hardly changes. When the fill level is 0.4 times the cylinder diameter, the 160D two-flat-blade mixer has good mixing performance with high mixing efficiency. The circumferential velocity has the greatest effect on mixing performance for side-by-side initial loading.