- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
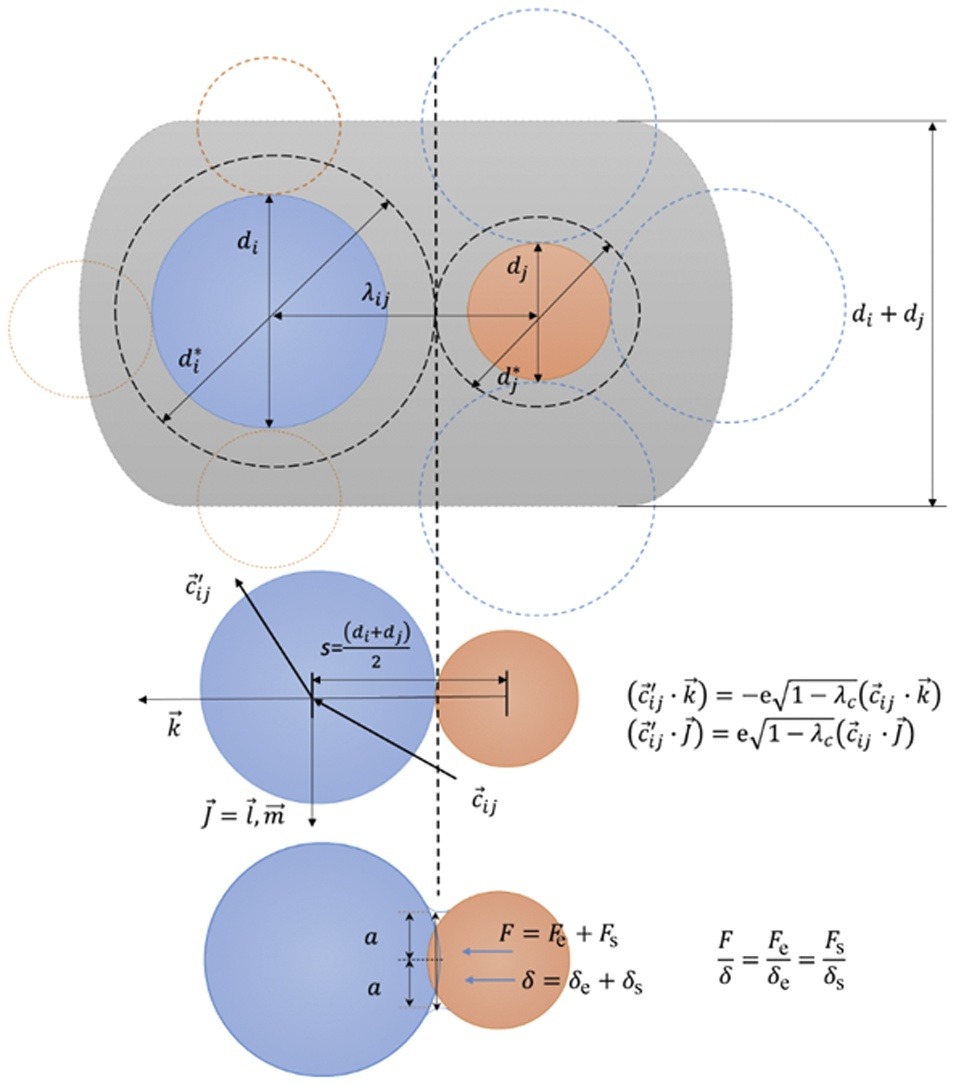
• A particle‒particle drag model is extended to cohesive particles flow.
• Mixing of binary particles (Geldart-A and C particles) was simulated.
• Three scales of mixing processes were observed.
A particle‒particle (p‒p) drag model is extended to cohesive particle flow by introducing solid surface energy to characterize cohesive collision energy loss. The effects of the proportion of cohesive particles on the mixing of binary particles were numerically investigated with the use of a Eulerian multiphase flow model incorporating the p‒p drag model. The bed expansion, mixing, and segregation of Geldart-A and C particles were simulated with varying superficial velocities and Geldart-C particle proportions, from which we found that the p‒p drag model can reasonably predict bed expansion of binary particles. Two segregation types of jetsam-mixture-flotsam and mixture-flotsam processes were observed during the fluidization processes for the Geldart-A and C binary particle system. The mixing processes of the binary particle system can be divided into three scales: macro-scale mixing, meso-scale mixing, and micro-scale mixing. At a constant superficial velocity the optimal mixing was observed for a certain cohesive particle proportion.