- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
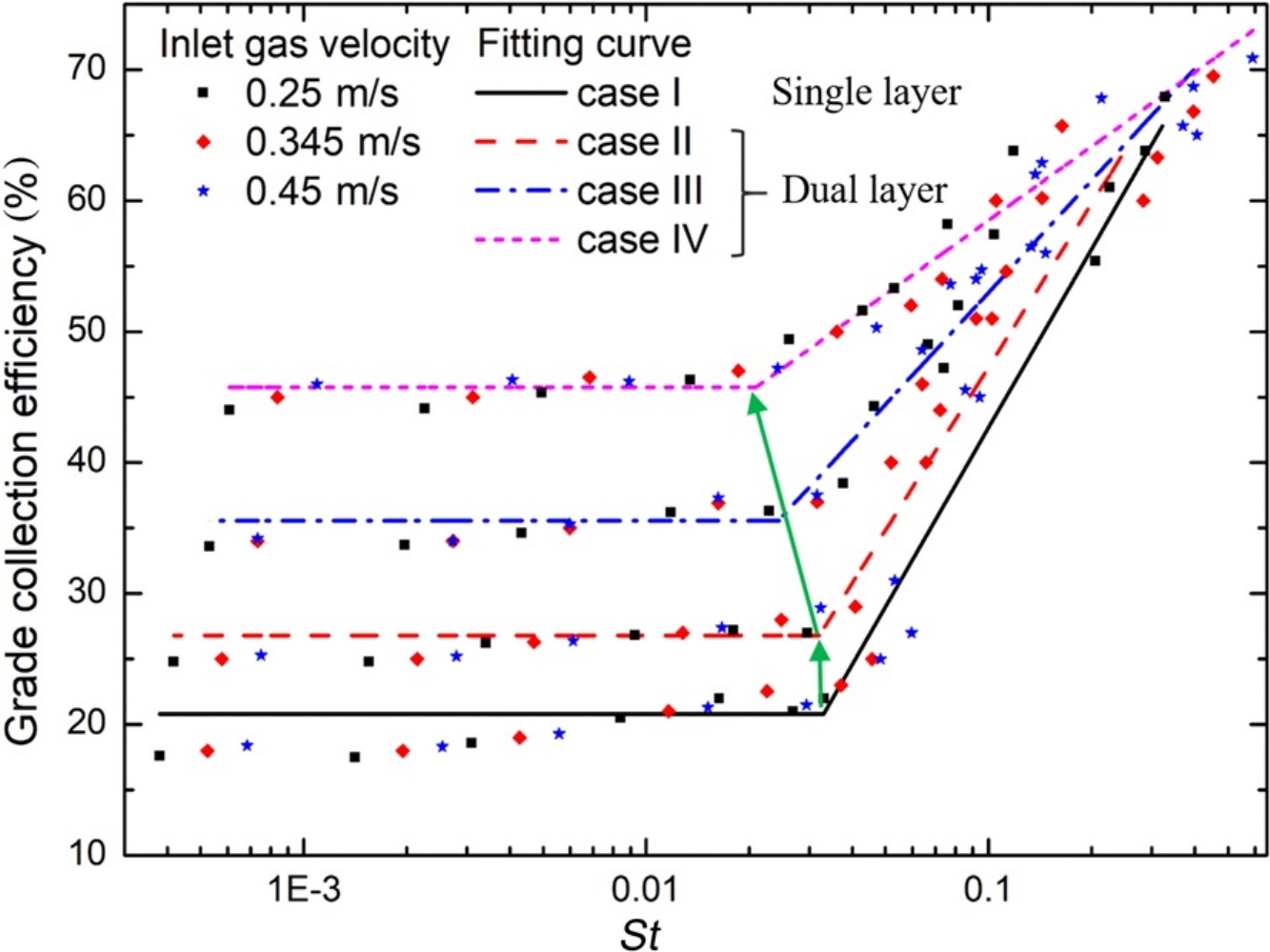
Collection efficiency in a three-dimensional randomly arranged dual-layer granular bed filter
• Collection efficiency is better for dual-layer than for single-layer granular beds.
• Inlet gas velocity affects grade collection efficiency less for dual-layer granular bed.
• St threshold shifts forward as bed depth of lower layer of fine granules increases.
The dual-layer granular bed filter packed with randomly arranged granules was simulated to study the effects of bed depth of the lower layer of fine granules and the inlet gas velocity on the collection mechanism. The computational results show that the collection efficiency is much better from this granular bed than a single-layer granular bed, especially for particle diameters of 1–10 μm. The inlet gas velocity has less effect on the grade collection efficiency of the dual-layer granular bed than of the single-layer granular bed. The dual-layer granular bed provides a high collection efficiency and low pressure drop. The relationship between the grade collection efficiency and the Stokes number (St) based on the inlet gas velocity is obtained. If St is below a threshold, the grade collection efficiency remains stable; if St is in value above threshold, the grade collection efficiency increases linearly with lg(St). As the bed depth of the lower layer of fine granules increases, the threshold for St shifts forward.