- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
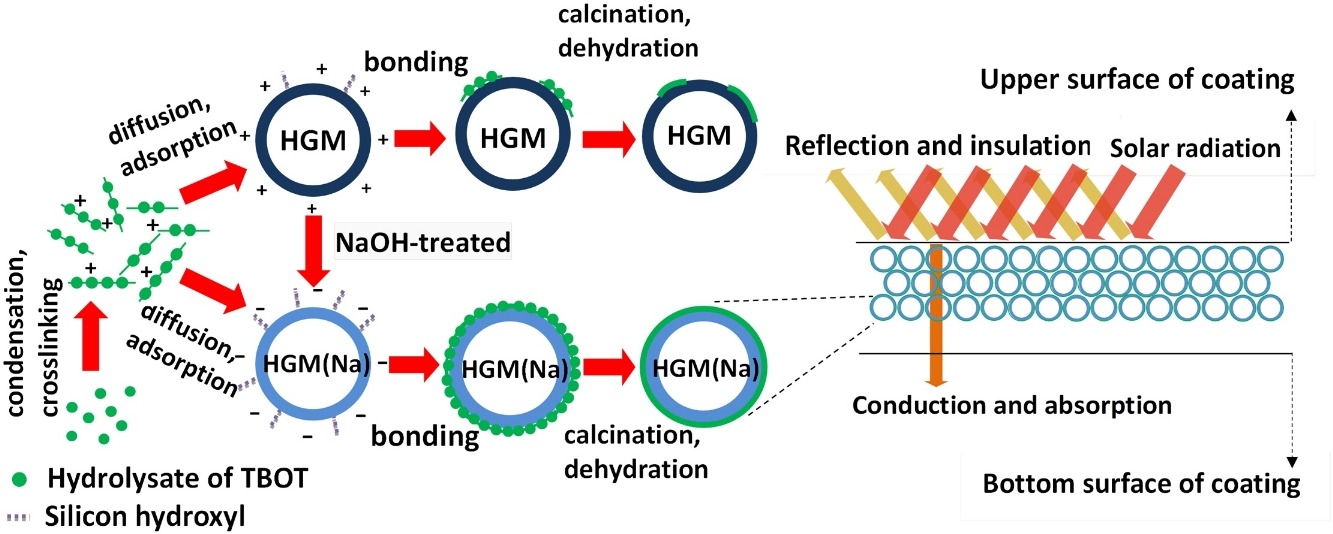
• TiO2 loading on hollow glass microsphere (HGM) was controlled by ethanol addition and coating number.
• Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic forces gave close contact between HGMs and TiO2.
• 15.9% loading of TiO2 yielded optimum reflective thermal insulation properties.
Hollow glass microspheres (HGMs) have great potential in building energy-saving and industrial insulation. Anatase TiO2-modified HGMs were prepared by a sol‒gel method in acetic acid-ethanol solution. Scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, zeta-potential measurements, nitrogen-sorption measurements, and Fourier-transform infrared and ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopies showed that the alkali modification of the HGMs greatly influenced the loading and microstructure of the TiO2 film. The TiO2 loading could be accurately controlled by ethanol addition and the TiO2 coating time. A mechanism for the TiO2 coating of the HGM surface is proposed. The synergistic action of hydrogen bonding and electrostatic forces resulted in close contact between the HGMs and TiO2 sol at pH 3.5. The effects of different TiO2 loading rates on the reflective and thermal insulation properties were studied. The near-infrared reflectance of 15.9% TiO2 coated on HGMs was 96.27%, and the inner surface temperature of the composite pigment coated on aluminum board was reduced by 22.4 °C. The TiO2/HGM composite pigments exhibited excellent solar reflective and thermal insulation properties, so have potential in the construction of exterior walls and roofs.