- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
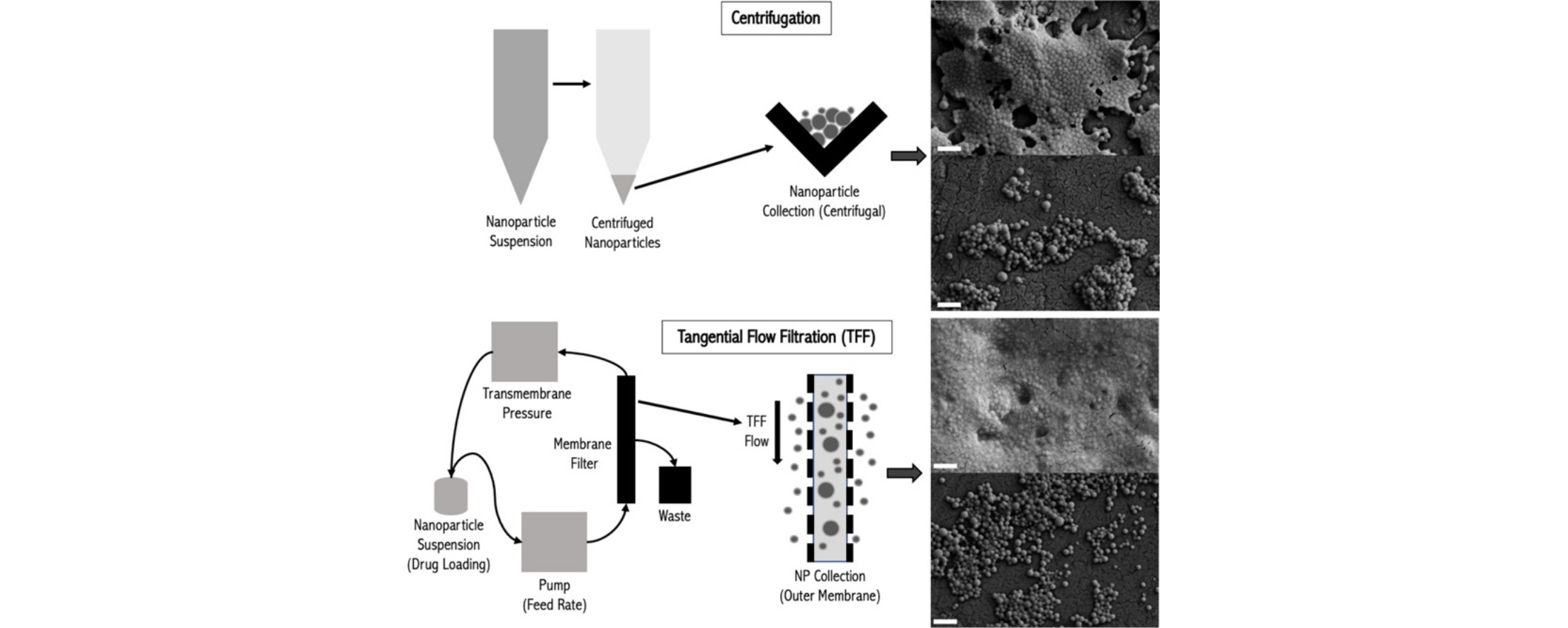
• TFF is a commonly used purification technique in particle engineering.
• There is a lack of understanding of the effect of TFF parameters on NP properties.
• TFF parameters were optimized for NP purification.
• The optimized parameters were used to make NPs containing different model drugs.
• TFF resulted in smaller nanoparticles compared with centrifugation.
Tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a purification method commonly used in a multitude of fields, including particle engineering. Currently, there is still a lack of comprehensive understanding of the effects of key TFF parameters on nanoparticle (NP) characteristics (purification outcomes). The present study aimed to investigate the influence of various factors on the characteristics of TFF-purified NP. The most commonly used NP purification method, centrifugation, was studied as a control. A design of experiment approach was implemented to investigate the influence of transmembrane pressure, flow rate, and initial drug loading on NP characteristics using paclitaxel as a model small molecule. Following the determination of optimized TFF parameters, the two purification methods were assessed using other model small molecules (i.e. tacrolimus and resveratrol). The results indicated that the TFF parameters and initial loading of the drug played important roles in the purified NP outcomes. Compared with the centrifugation method, TFF resulted in smaller NP with higher drug loading. TFF was able to circumvent issues associated with conventional centrifugation, while yielding similar results, and can potentially serve as a suitable large-scale purification method for polymeric NP.