- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Impact of non-spherical particles on nano-aluminum burning behavior was examined.
• Particle shape and size play a significant role in combustion performance.
• Reasonable agreement between simulation results and experimental data was obtained.
• Current models should be adapted for non-spherical nano-aluminum combustion.
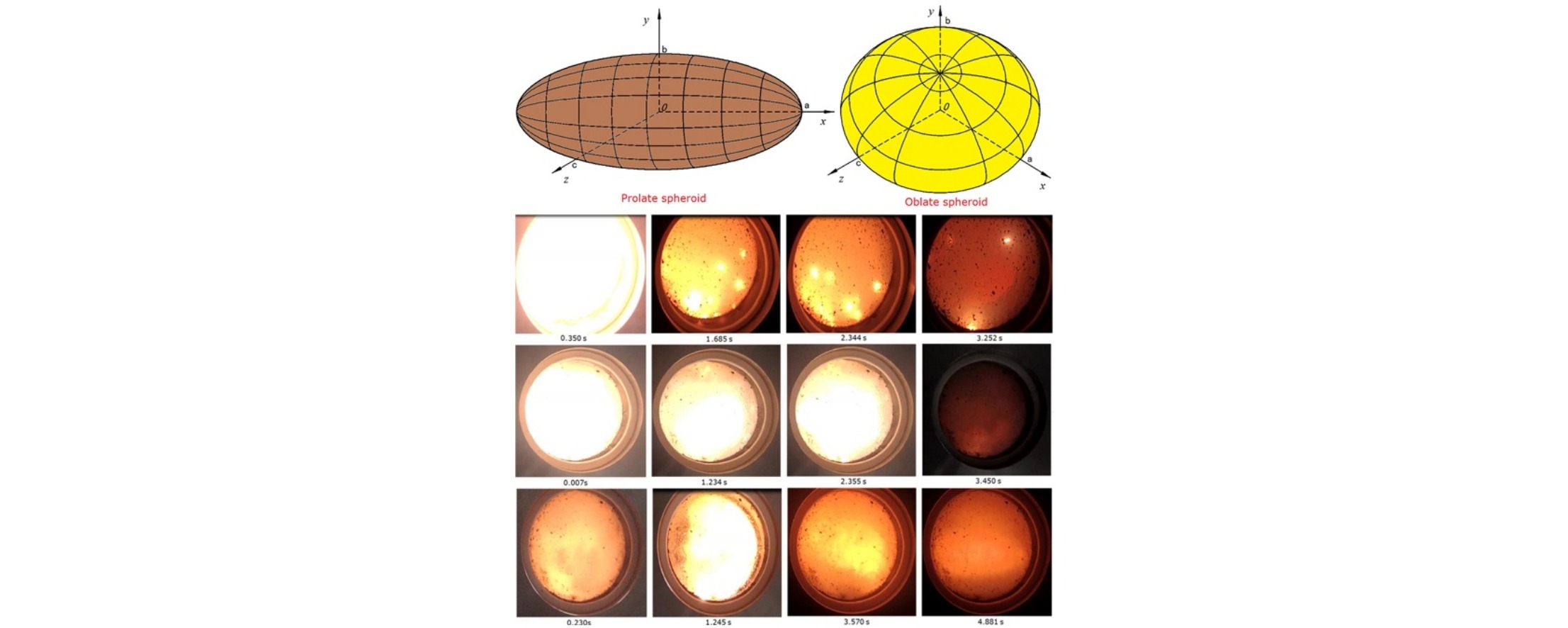
The shape of an aluminum particle is assumed to be spherical or an equivalent sphere during the combustion process. Such an assumption lacks objectivity and leads to unreasonable approximations of burning efficiency and performance. To investigate the influence of non-spherical particles on burning behavior, this study focused on a theoretical and experimental investigation of the combustion of nanoscale aluminum ellipsoidal particles. Models for prolate and oblate spheroids in aluminum combustion were established to explore combustion properties such as mass release rate, linear burning rate, burning rate, and burnout time. To validate the theoretical results, combustion experiments were conducted on three samples. Reasonable agreement between the results of numerical simulation and experimental findings was obtained in terms of the particle burning characteristics. It was found that particle morphology (such as prolate or oblate spheroid shape) and size play a significant role in the combustion performance of nanosized aluminum particles.