- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
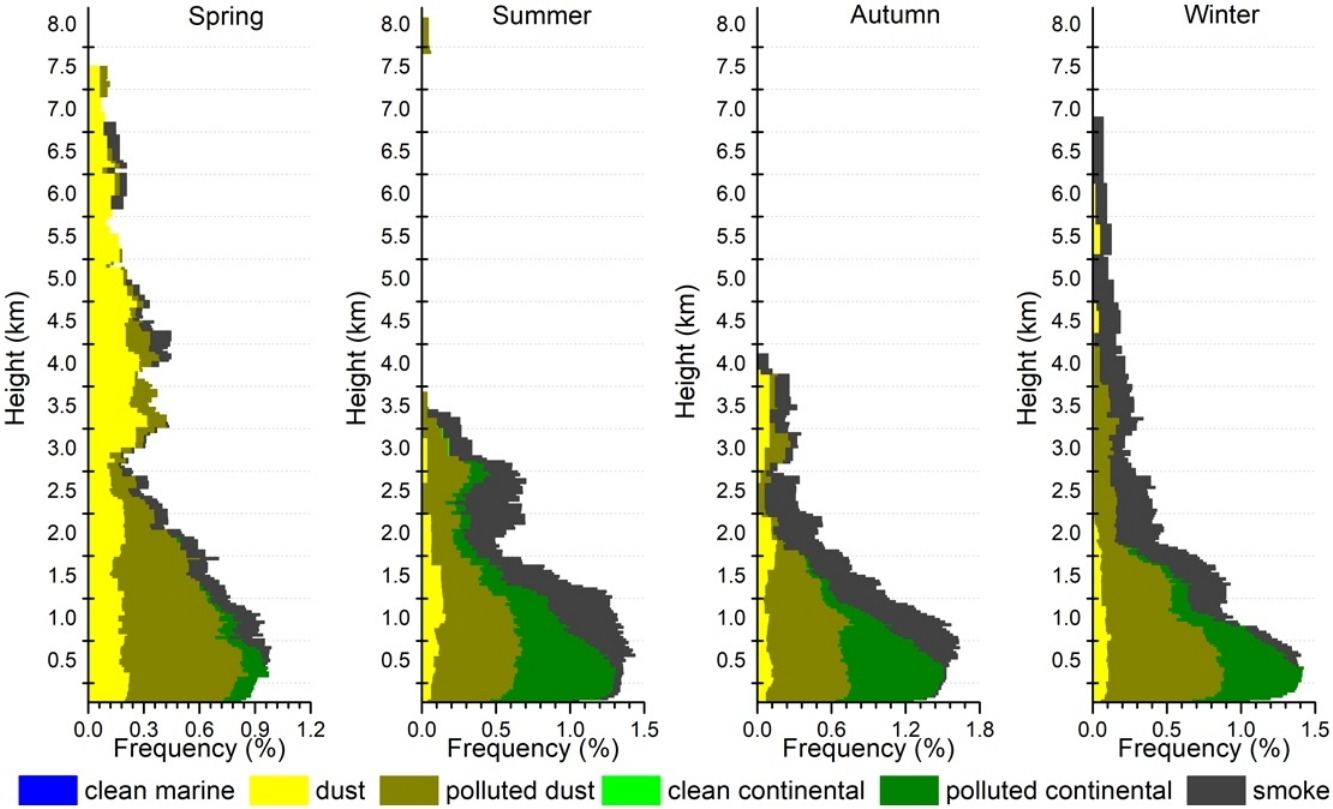
• Polluted dust, polluted continental and smoke aerosols were the main aerosol types.
• High numbers of fine secondary particles contributed to high AOD values in summer.
• Smoke aerosols relating to local/regional pollution occurred at high altitudes in winter.
Although the concentration of atmospheric particulate matter in Shanghai has declined in recent years, aerosols remain one of the major pollutants affecting air quality. Herein, spatio-seasonal variation in aerosol optical properties and aerosol types were studied over a 10-year period (2006–2015) in Shanghai, China, using satellite data from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP). The average aerosol optical depth values for central urban and suburban areas of Shanghai were between 0.9 and 1.0. Clear seasonal variation in aerosol concentrations occurred, causing strongest attenuation in summer and weakest attenuation in autumn. Polluted dust, polluted continental (urban/industrial) and smoke aerosols were the main aerosol types. Desert dust aerosols occurred in the Shanghai area at higher altitudes (greater than 3 km) in spring, related to dusty weather in the north; while in winter, smoke aerosols occurred at high altitudes, related to haze pollution in the north. The aerosols detected in autumn were mainly from local sources, comprising polluted dust, polluted continental, and smoke aerosols. Aerosols in Shanghai clearly reflect both local and regional sources at different times.