- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Three differently prepared AuNPs were functionalized with amino acids.
• Chemical reduction did not produce nanoparticles suitable for functionalization.
• Biogenic AuNPs were the most suitable for functionalization.
• Bacteria-mediated AuNP biogenesis enabled functionalization with six amino acids.
• pH of the functionalization reaction influences AuNP size/electrophoretic mobility.
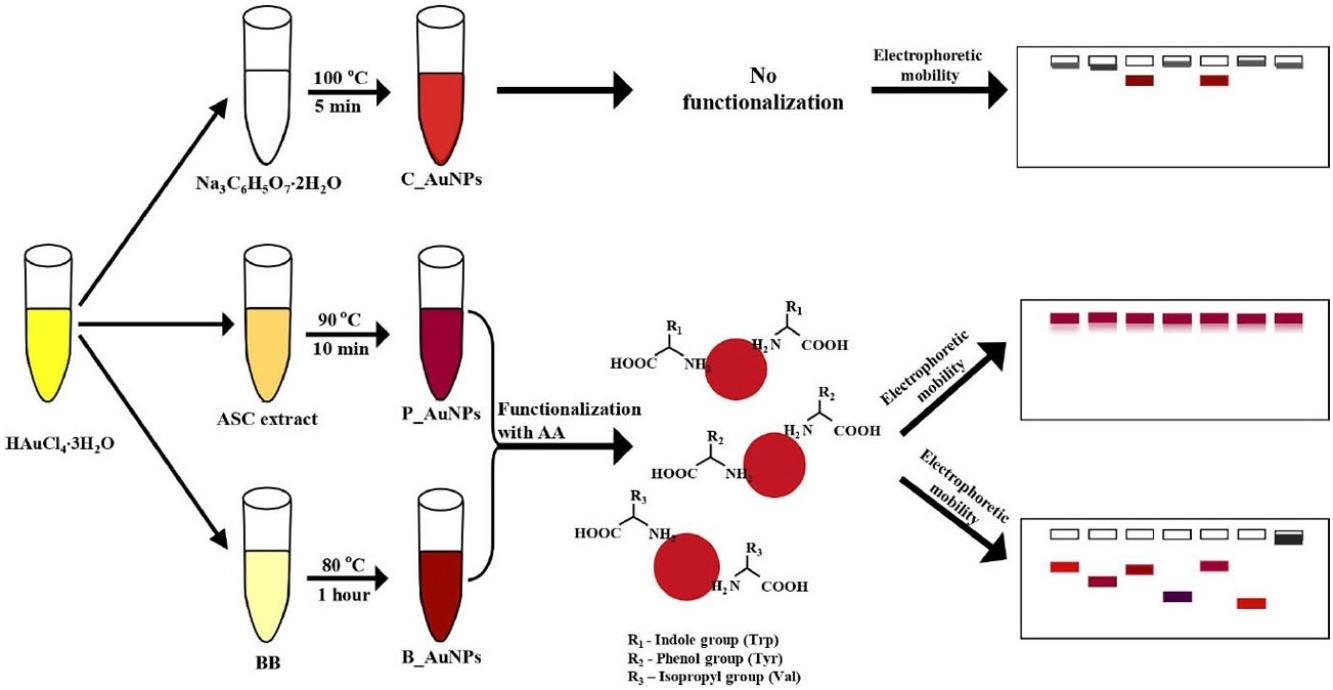
The potential utility of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) synthesized via different methods for biomedical applications vary greatly due to inherent differences in their surface properties. In the present study, we investigated the functionalization of AuNPs synthesized by chemical reduction, plant extract, and bacteria-mediated methods with 22 l-amino acids. Nanoparticles produced by bacteria-mediated (B_AuNPs) and plant-mediated (P_AuNPs) methods showed good potential, as they were able to be functionalized with six (histidine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine) and four (cystine, tryptophan, tyrosine, and valine) amino acids, respectively. In contrast, AuNPs produced by chemical reduction (C_AuNPs) were not found to be suitable for functionalization. Optimal functionalization conditions were found to be amino acid concentration of 20–25 mM and neutral pH (7) for P_AuNPs, whereas B_AuNPs tolerated more variable conditions. The electrophoretic mobility of P_AuNPs after functionalization indicated that these nanoparticles were less sensitive than B_AuNPs to the deviations from optimal conditions. A significant change in mobility was observed when B_AuNPs were functionalized with either methionine or tryptophan. Overall, the results of this study suggest that the suitability of the three differently synthesized AuNPs with amino acids is in the following order: B_AuNPs > P_AuNPs > C_AuNPs.