- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
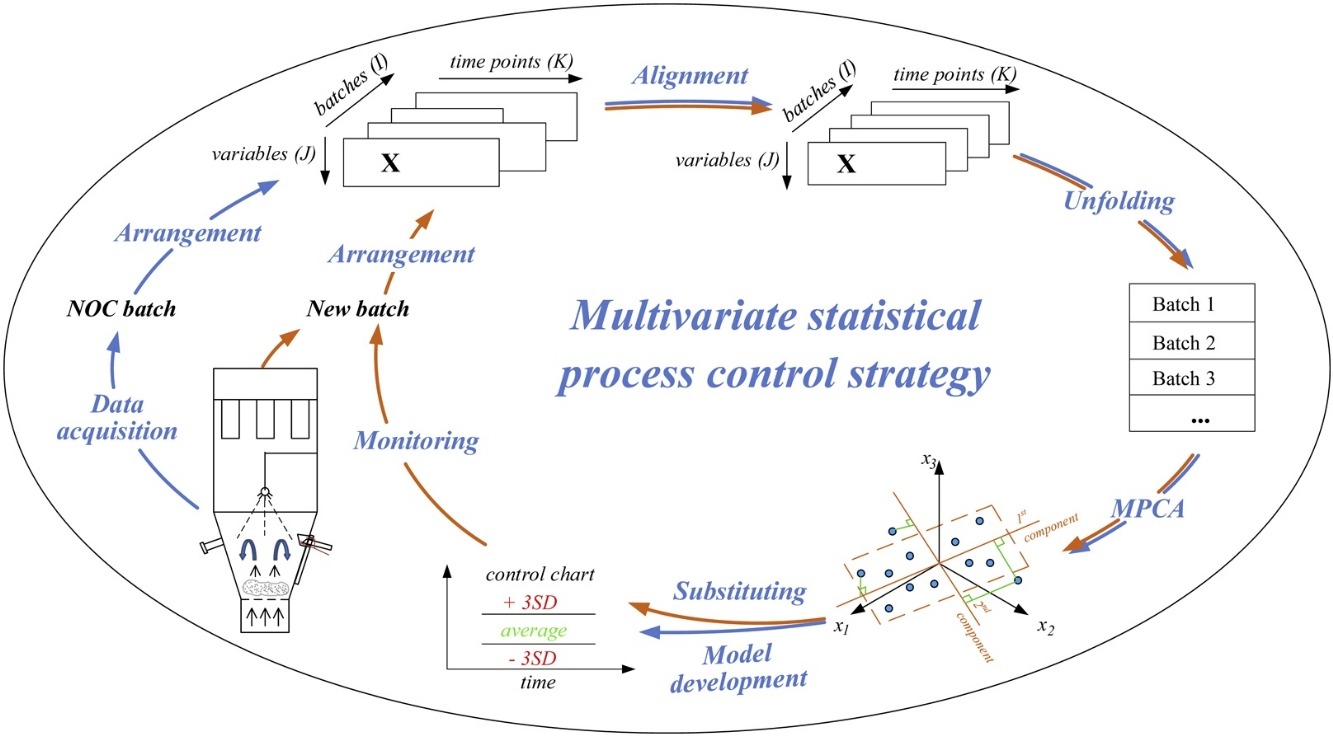
• Monitoring and fault diagnosis in pulsed-spray fluid bed granulation were studied.
• Multivariate statistical process control (MSPC) was used to monitor granulation.
• Correlation optimized warping synchronized time-varying process batch trajectories.
• Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy with MSPC was used as a quality control strategy.
• NIR spectroscopy-based multivariate process trajectories were proposed for granulation.
Pulsed spray is a useful tool for granule size control in fluid bed granulation. To improve the quality control of pulsed-spray fluid bed granulation, a combination of in-line near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and principal component analysis was used to develop multivariate statistical process control (MSPC) charts. Different types of MSPC charts were developed, including principal component score charts, Hotelling's T2 control charts, and distance to model X control charts, to monitor the batch evolution throughout the granulation process. Correlation optimized warping was used as an alignment method to deal with the time variation in batches caused by the granulation mechanism in MSPC modeling. The control charts developed in this study were validated on normal batches and tested on four batches that deviated from normal processing conditions to achieve real-time fault analysis. The results indicated that the NIR spectroscopy-based MSPC model included the variability in the sample set constituting the model and could withstand external variability. This research demonstrated the application of synchronized NIR spectra in conjunction with multivariate batch modeling as an attractive tool for process monitoring and a fault diagnosis method for effective process control in pulsed-spray fluid bed granulation.