- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
Maha Al-Ali, Rajarathinam Parthasarathy *
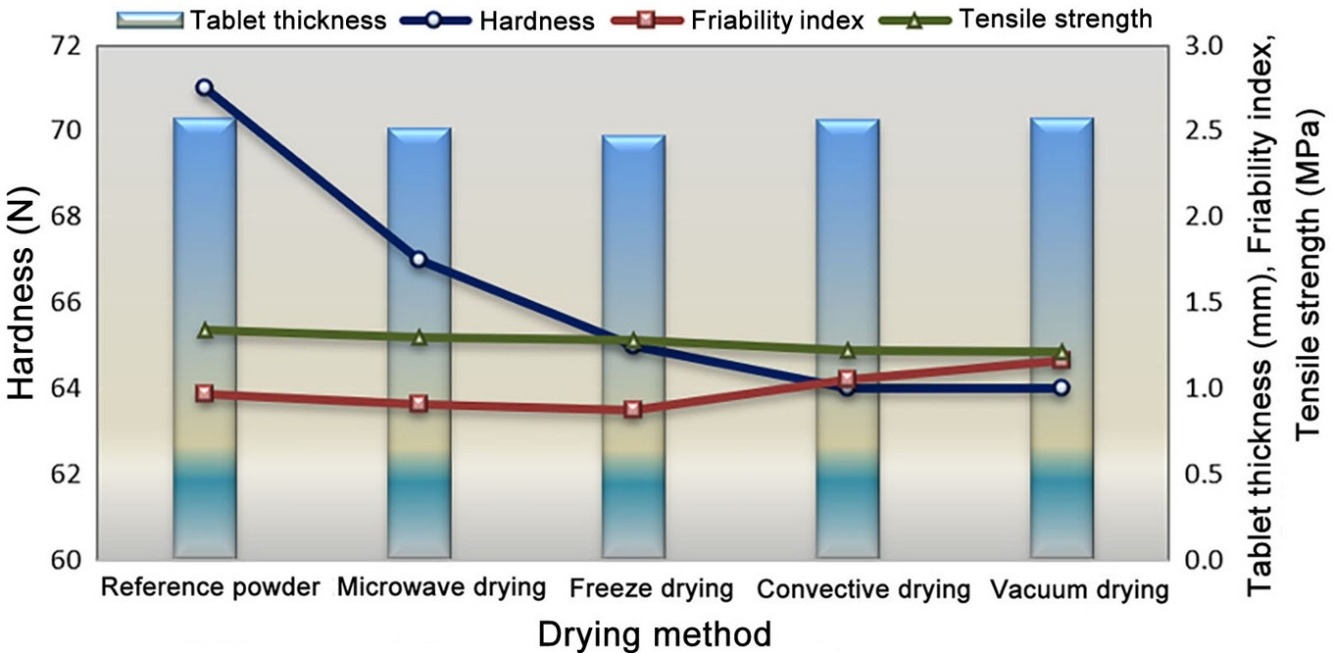
• Microwave dried tablets exhibit the second-highest tensile strength and hardness.
• The friability of tablets subjected to microwave drying is within accepted limits.
• Naproxen sodium tablets produced using microwave drying have acceptable mechanical properties.
• Enhancement or degradation in the mechanical properties of tablets depends on the drying method used.
Tablets are one of the most commonly used solid dosage forms taken by patients. The preparation of high-quality tablets requires an understanding of the preparation process and elucidation of how the physical and mechanical properties change as a function of the preparation process. This work aims to investigate the impact of microwave irradiation drying and conventional drying methods (including freeze, convective and vacuum drying) on the hardness, tensile strength and friability of tablets made from a multi-component formulation containing naproxen sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, and polyvinylpyrrolidone. The results show that tablets subjected to microwave drying had the second-highest tensile strength and hardness of 1.296 MPa and 67 N, respectively. The tablets subjected to vacuum drying had the lowest tensile strength and hardness of 1.21 MPa and 64 N, respectively. The friability index values for the tablets derived from the microwave and freeze-drying methods were <1%, while those for the tablets subjected to convective drying and vacuum drying methods were>1%. Microwave drying was observed to be an efficient method to produce naproxen sodium-containing tablets with satisfactory mechanical properties. These findings confirm that the drying method plays an essential role in the improvement or degradation of the mechanical properties of tablets.