- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Particle resuspension due to surface vibration was investigated.
• An external vibrating force was considered to apply normal on a thin plate.
• Oscillations in the vertical direction were propagated through bending waves.
• Particle motion was initiated provided that inertia due to its mass was overcome.
• A force balance method was used to investigate whether particle resuspension occurred.
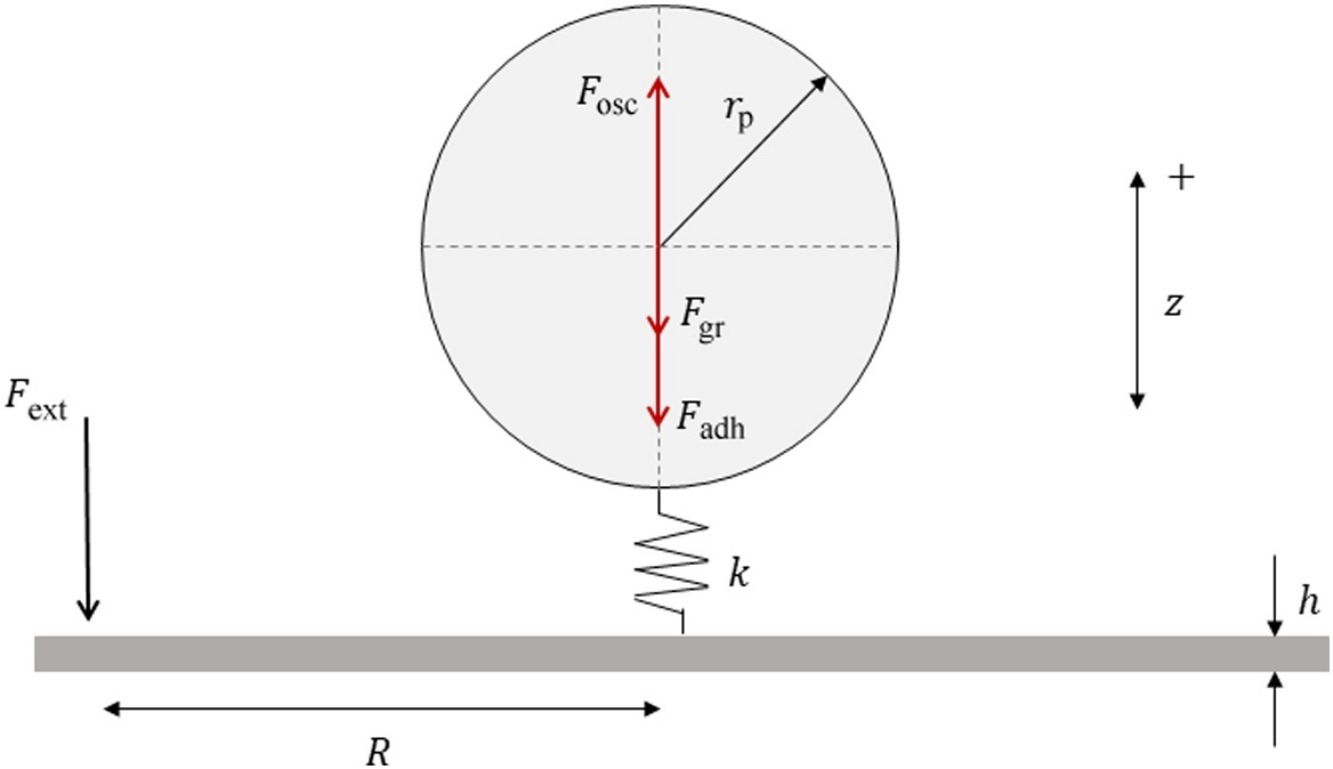
In this study, particle resuspension due to surface vibration was investigated. A spherical particle was assumed to rest on top of a thin plate, and an external vibrating force was applied normal on the plate at t = 0 and at distance R from the particle. The external driving force created a displacement field in both time and space domains, where deformations in the body of the plate were considered small elastic oscillations that are perpendicular to the propagation of the displacement. Free oscillations were introduced via the theory of elasticity and the creation of waves on thin plates, i.e., bending waves. Particle motion in the vertical direction was initiated through plate displacement, provided that inertia due to particle mass is overcome. In particular, the particle was assumed to oscillate with a force (of oscillation) estimated via Newton’s second law of motion, comprising of two components: the acceleration due to the plate displacement and the particle mass. Subsequently, a simple force balance method was used to determine the conditions for resuspension. Accordingly, resuspension occurs when the oscillation force exceeds the couple of the adhesive and gravitational forces. The results suggest that the plate displacement depends on the characteristics of the applied force, material properties, and plate thickness. In addition, it was found that the oscillation force is substantially lower than the applied force and that it depends on plate displacement and particle mass. Additionally, the particle size significantly influencedthe outcome of resuspension. Thus, resuspension is favorable for large particles, strong applied forces, and high forcing frequencies.