- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
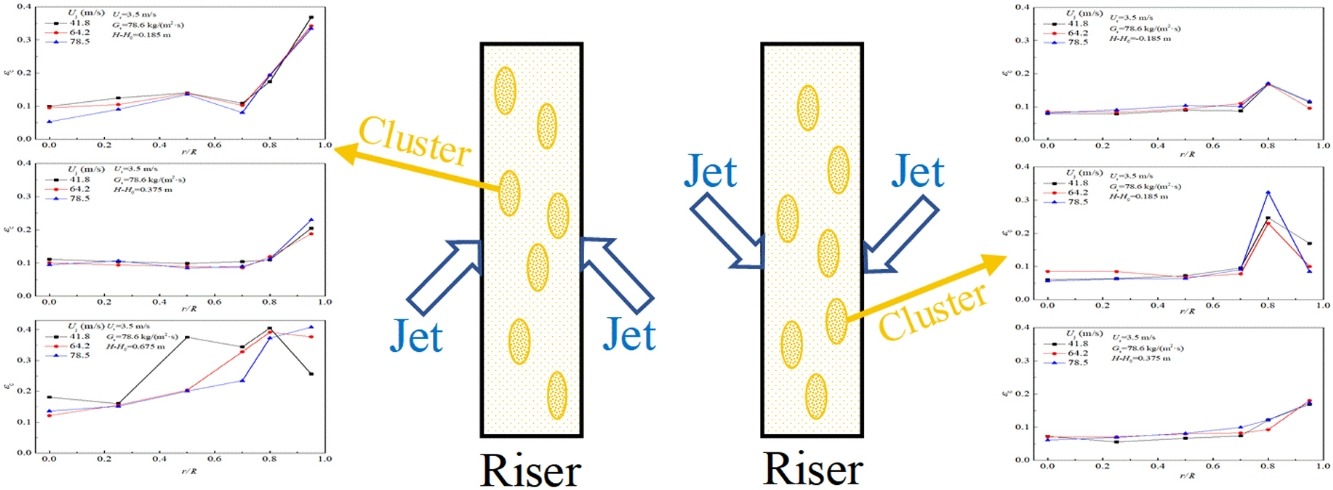
• Solid holdup inside clusters and its distribution range in jet mixing zone were obtained.
• Effect of jet velocity on the distribution of solid holdup inside clusters was analyzed.
• Advantages of downward jets were shown based on cluster characteristics.
By analyzing solid holdup signals in the jet influence zone of risers, the characteristics of clusters were studied. The solid holdups inside clusters and their distribution ranges were calculated under the cases of both upward and downward feed jets. Moreover, the effects of the jet velocity on the cluster characteristics were analyzed. The solid holdups inside clusters have higher values and wider distribution ranges in the upward feed injection zone than in the downward zone, implying that the number of individual particles in a cluster is unstable under the influence of upward jets. For the case of downward jets, cluster formations in the jet influence zone of risers can more easily maintain stability, offering a better mixing environment for jets and particles. As the jet velocity increases, the solid holdups inside clusters in the riser wall of the upward injection zone increase accordingly, while the distributions of solid holdups inside clusters have no significant changes if the feed jets are downward. This phenomenon confirms that improved operational flexibility can be obtained if downward jets are mixed with the prelift gas–solid flow in risers.