- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
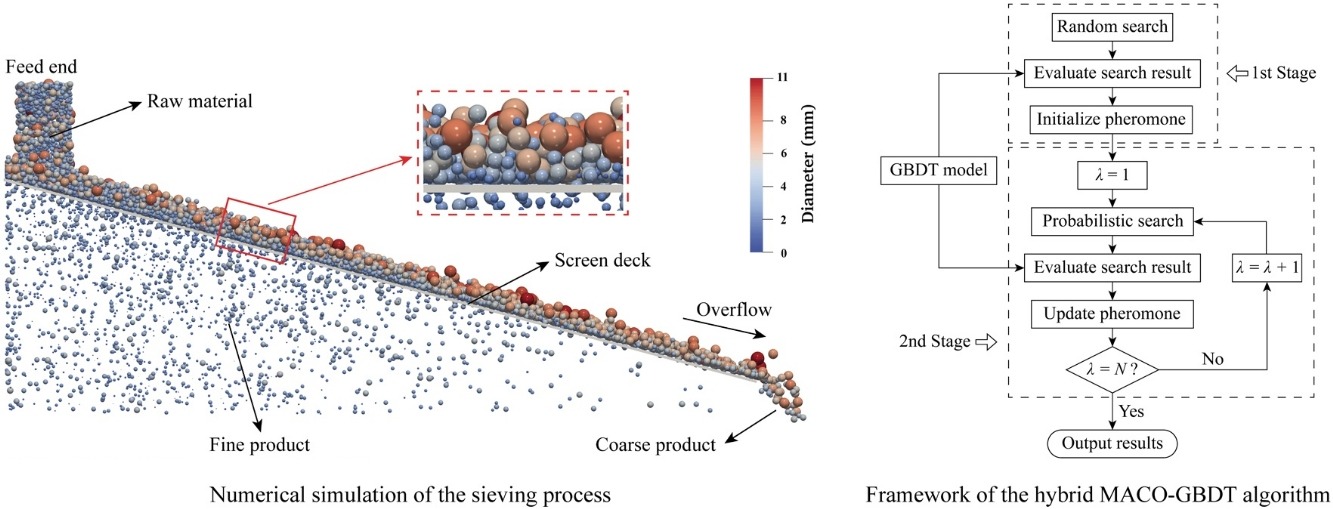
• The sieving process is numerically simulated based on the Discrete Element Method (DEM).
• The Gradient Boosting Decision Trees (GBDT) algorithm is introduced for the prediction of sieving results.
• A hybrid MACO-GBDT algorithm is proposed for the optimization of sieving performance.
• The reliability of MACO-GBDT algorithm is verified by the numerical experiments.
As a typical screening apparatus, the elliptically vibrating screen was extensively employed for the size classification of granular materials. Unremitting efforts have been paid on the improvement of sieving performance, but the optimization problem was still perplexing the researchers due to the complexity of sieving process. In the present paper, the sieving process of elliptically vibrating screen was numerically simulated based on the Discrete Element Method (DEM). The production quality and the processing capacity of vibrating screen were measured by the screening efficiency and the screening time, respectively. The sieving parameters including the length of semi-major axis, the length ratio of two semi-axes, the vibration frequency, the inclination angle, the vibration direction angle and the motion direction of screen deck were investigated. Firstly, the Gradient Boosting Decision Trees (GBDT) algorithm was adopted in the modelling task of screening data. The trained prediction models with sufficient generalization performance were obtained, and the relative importance of six parameters for both the screening indexes was revealed. After that, a hybrid MACO-GBDT algorithm based on the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) was proposed for optimizing the sieving performance of vibrating screen. Both the single objective optimization of screening efficiency and the stepwise optimization of screening results were conducted. Ultimately, the reliability of the MACO-GBDT algorithm were examined by the numerical experiments. The optimization strategy provided in this work would be helpful for the parameter design and the performance improvement of vibrating screens.