- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
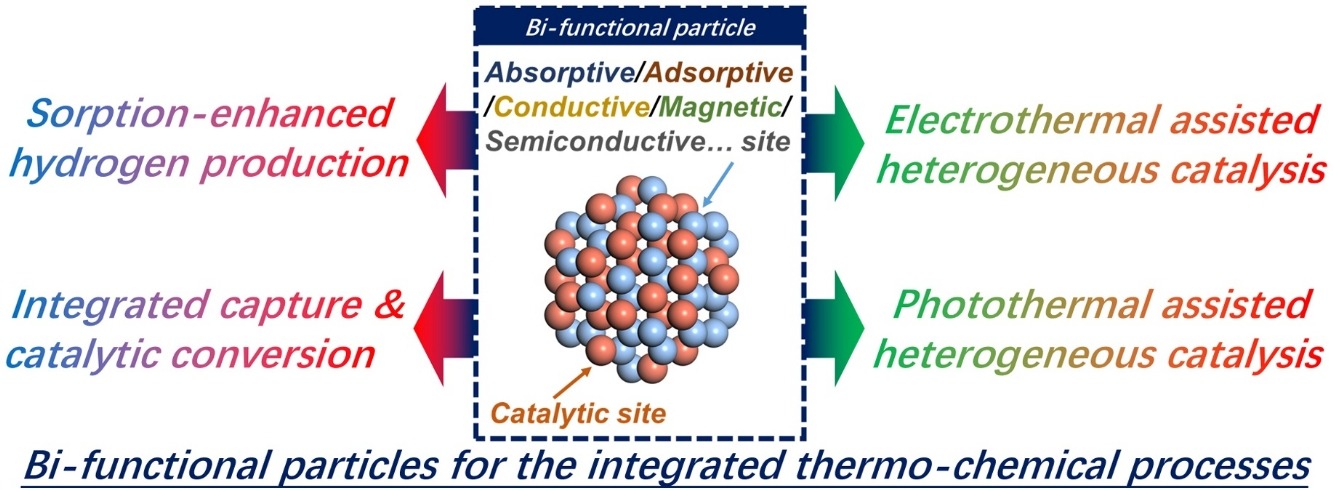
• Particulate catalysts with adsorptive/ heating feature are bi-functional particles.
• Bi-functional particles for integrated reaction-separation are reviewed in detail.
• Bi-functional particles for integrated heating-reaction are also briefly reviewed.
• Bi-functional particles are feasible in integrated thermo-chemical processes.
Particulate materials possessing dual functionalities have received tremendous investigations in many fields, owing to their superiority over mono-functional counterparts and their potential for process integration and intensification. This review focuses on bi-functional catalytic particles which also serve as sorbents/adsorbents or heat suppliers in the scheme of various thermo-chemical processes, enabling inherent separation or energy conservation within single-step operation. Bi-functional particles applied for integration of reaction and separation including sorption-enhanced hydrogen production and integrated capture and catalytic conversion processes are reviewed in detail, providing insights into material design and key performance indicators. On the other hand, bi-functional particles applied for integration of reaction and non-thermal radiation heating, including electrothermal and photothermal assisted heterogeneously catalyzed reactions, are also reviewed, with emphasis on the material property and energy efficiency improvement. These bi-functional particles show broad adaptability and feasibility in various reactions operated in integrated and intensified schemes, affording huge potentials for further improving productivity and efficiency in thermo-chemical processes.