- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
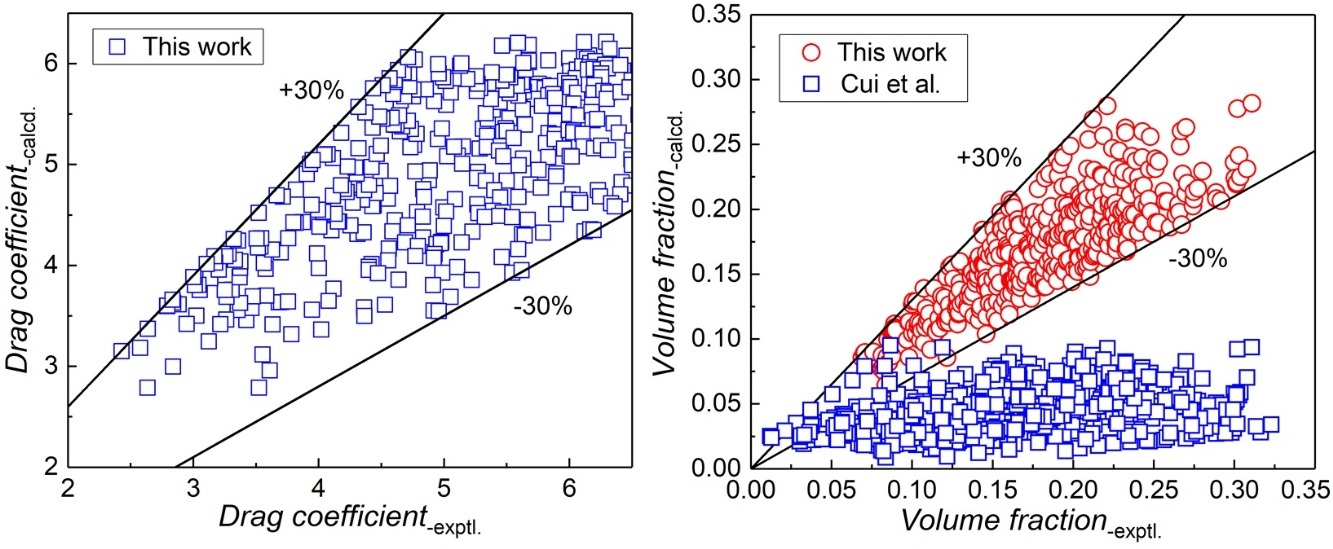
• Correlations of drag coefficient and volume fraction of bubbles in SCWFBs are demonstrated.
• The effect of the operating conditions on drag coefficient and volume fraction is discussed.
• Dual-capacitance probe system is applied for measuring bubble hydrodynamics.
The supercritical water fluidized bed (SCWFB) is a recently introduced reactor for biomass gasification that does not release pollutants. Four groups of Geldart B-type quartz sands with different particle sizes were fluidized at a system pressure of 20–27 MPa and system temperature of 410–570 °C. A series of experiments were performed for determining the drag coefficient and volume fraction of bubbles. The effects of the particles’ size, superficial velocity, system pressure, and temperature on the drag coefficient and volume fraction are discussed. In addition, a correlation between experimental and computed values is demonstrated for both the drag coefficient and volume fraction in SCWFBs. The relative error of the correlation is within ±30%. The results of this study provide significant guidance for the scaling-up design of SCWFBs and for the development of supercritical water gasification technology.