- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
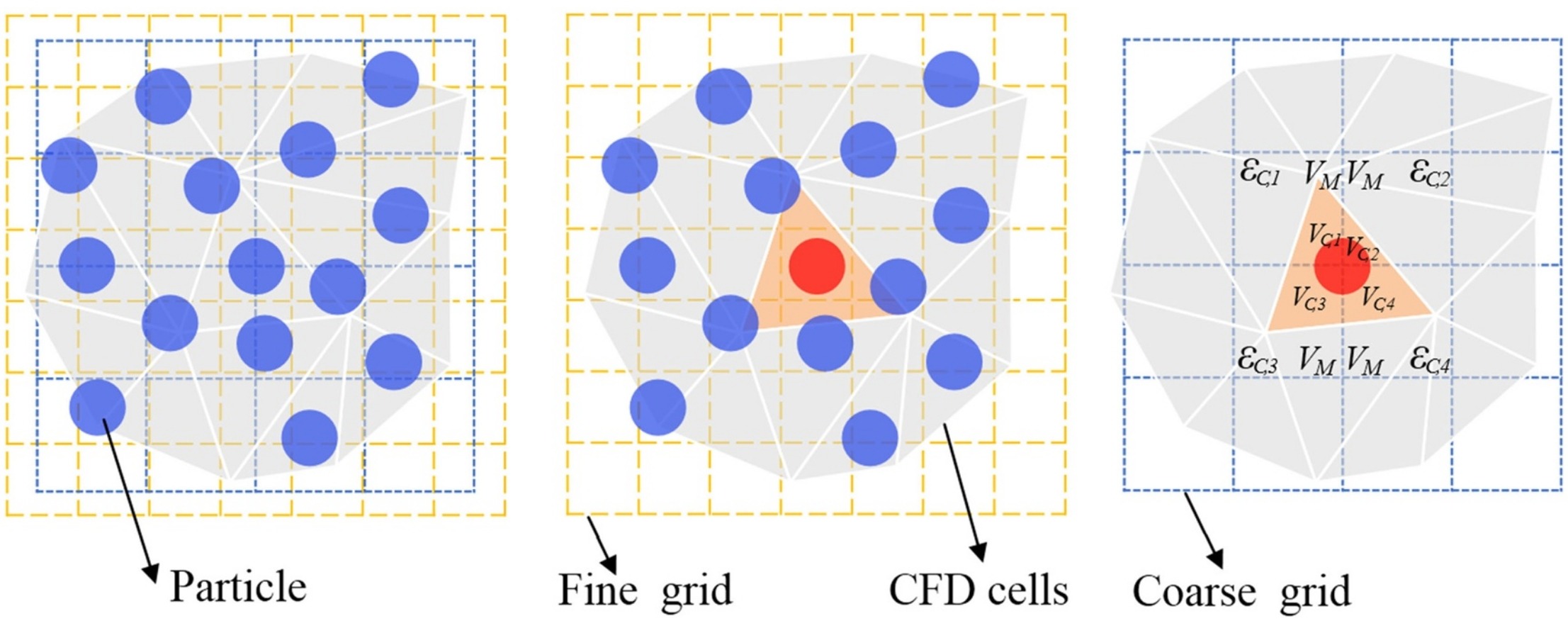
• A novel virtual dual-grid model is first proposed to accelerate CFD-DEM simulation.
• CFD-DEM-VDGM model is used to simulate fluidization behavior of 4.2 million particles.
• The volume fraction calculation speed is increased more than 10 times in complex geometry.
• The improved particle data transfer pattern can save more than 90% of the data transfer time.
• The scale-up law of FB-CVD process was proposed based on volume fraction distribution.
The simulation of particle fluidization behavior in a complex geometry with a large number of particles is challenging owing to the complexity of unstructured computational grids and high computational intensity. In this study, a virtual dual-grid model (VDGM) is proposed to calculate the solid volume fraction in unstructured grids and speed up the calculation. The VDGM is coupled with a computational fluid dynamics–discrete element method model to simulate particle fluidization behavior in a multi-ring inclined-hole spouted fluidized bed with 4.2 million particles under a high temperature of 1423 K. A computational fluid dynamics–discrete element method–virtual dual-grid model (CFD–DEM–VDGM) coupling model is implemented based on commercial software Fluent and EDEM. The time step settings in Fluent and EDEM and the pattern of particle data transfer in Fluent are improved to speed up the calculation. It is discovered that the VDGM can calculate the solid volume fraction in unstructured grids of complex geometry and speed up the calculation effectively. The calculation speed increased by more than 10 times compared with that of the segmentation sampling method. The new pattern of particle data transfer in Fluent can reduce data transfer time by more than 90%. The fluidization behavior of 4.2 million high-density particles in the multi-ring inclined-hole spouted fluidized bed is obtained and analyzed in detail. The CFD–DEM–VDGM coupling method is validated for the bed expansion height and spouting cycle time in a spouted fluidized bed via experimental results.