- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
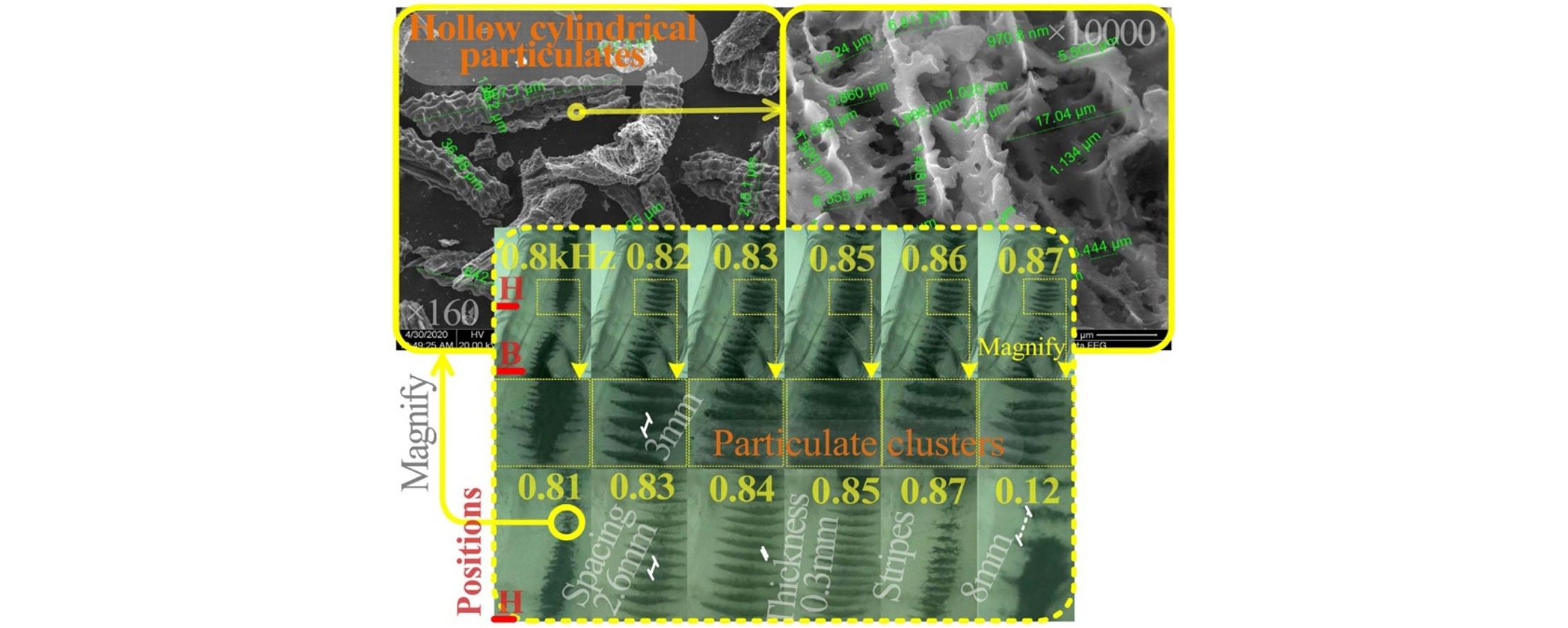
• Aggregation of smoke particulates in a modulated annular acoustic field is studied.
• Visualization and analysis of complex acoustic-particulate-fluid system are performed.
• Collective aggregation and fragmentation process of smoke particulates are demonstrated.
• Acoustic radiation force and secondary radiation force explain the process control.
• Physical parameter changes in the particles in different environments cause the behaviors.
The visualization and analysis of a novel acoustic-particulate system is the objective of this study. The system is composed of rice-husk fired smoke particulates (36.7 nm–840 μm) and one annular resonant circular-tube waveguide contrarily coupled with two sound sources. The collective interaction behavior process of smoke particulates in an inhomogeneous acoustic field is displayed during an experiment and a simulation. The result shows that the aggregation and fragmentation of particles under a change in resonant frequencies and sound pressure amplitude is extremely complex. This complex process consists of dynamically tuning the particle characteristics to attain stripes shaped like thin-films/umbrellas and clusters with volume-change/fragmentation. The balanced modulation of the acoustic radiation force and secondary radiation force to alter the particle characteristics (size and stack density) is verified to be the control mechanism of the particle system. The intermediate variable of the process control is the acoustic contrast factor (Ф) related to the physical characteristics of the growing particulates. The value plus-minus alternation of Ф results in different particulate processes. This study can enhance the application of aerodynamic acoustic-particulate-fluid systems for environment protection, energy fuel conversion, and industrial production.