- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Monodispersed PVP-stabilized gold nanoparticles produced in aqueous region.
• GNP nucleation and growth controlled by electrospray mist into liquid reaction.
• Electrospray flow rate, droplet size, and current affected properties of GNP.
• Electrospray droplet and Au3+ concentration influenced GNP size, morphology, and PDI.
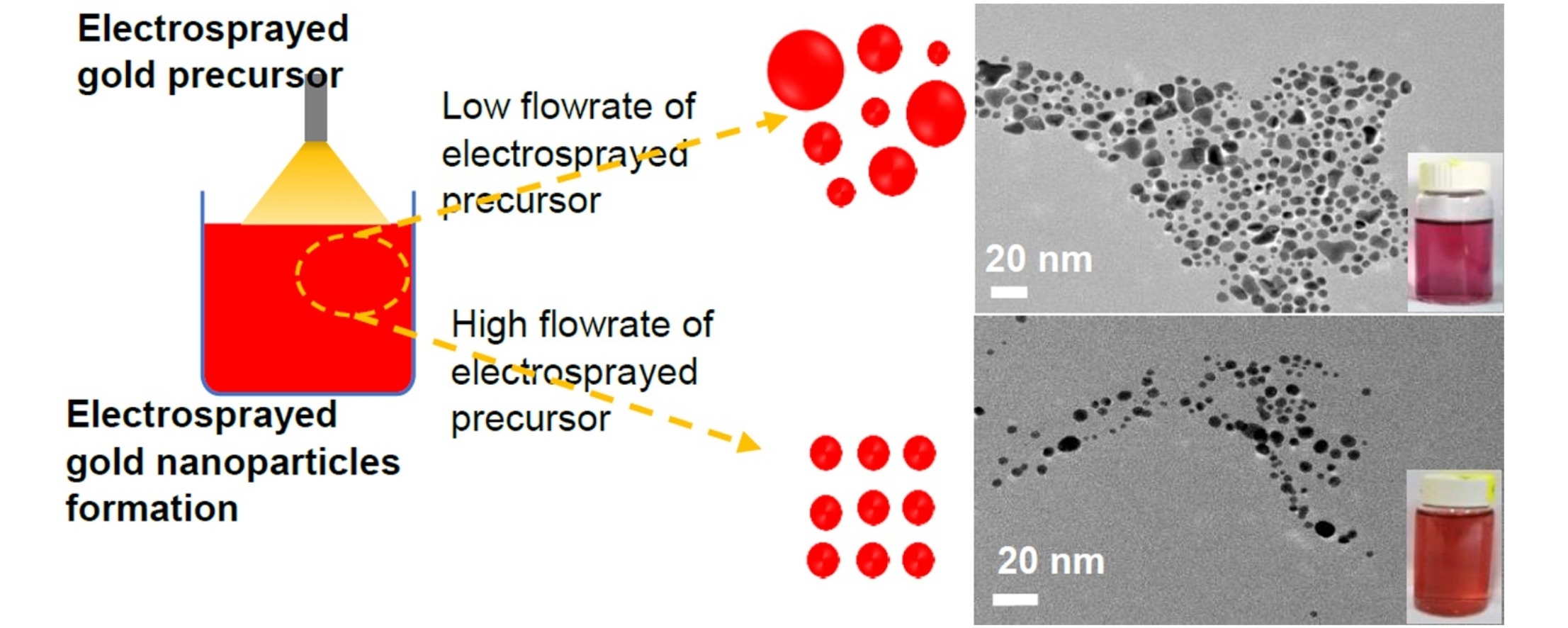
In this study, the controlled nucleation and growth of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) were investigated using a self-repelled mist in a liquid chemical reaction environment. An electrospray-based chemical reduction method was conducted in the aqueous region and at room temperature to synthesize the polymeric-stabilized gold nanoparticles. The electrospray technique was used to atomize a hydrogen tetrachloraurate (III) (HAuCl4) precursor solution into electrostatically charged droplets. The atomized droplets were dispersed in an aqueous reaction bath containing L-ascorbic acid as a reducing agent and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a stabilizer. The effect of the electrospray parameters, specifically the flow rate and electrospray droplet size, as well as the reaction conditions such as the concentration of reactants, pH, and stabilizer (PVP), were investigated. The mean diameter of the GNPs increased from around 4 to 9 nm with an increase in the electrospray flow rate, droplet size, and current passing through the electrospray jet. Spherical and monodispersed GNPs were synthesized at a relatively high flow rate of 2 mL/h and a moderate concentration of 2 mM of precursor solution. The smallest-sized GNP with a high monodispersity was obtained in the reaction bath at a high pH of 10.5 and in the presence of PVP. It is expected that continuous and mass production of the engineered GNPs and other noble metal nanoparticles could be established for scaling up nanoparticle production via the proposed electrospray-based chemical reduction method.