- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Multidimensional separation due to selective spherical agglomeration.
• X-ray microtomography (X-RMT) with graphite particles 1 μm–20 μm.
• Particle shape analysis with X-RMT images.
• Sphericity distribution of platelet and spherical graphite particles.
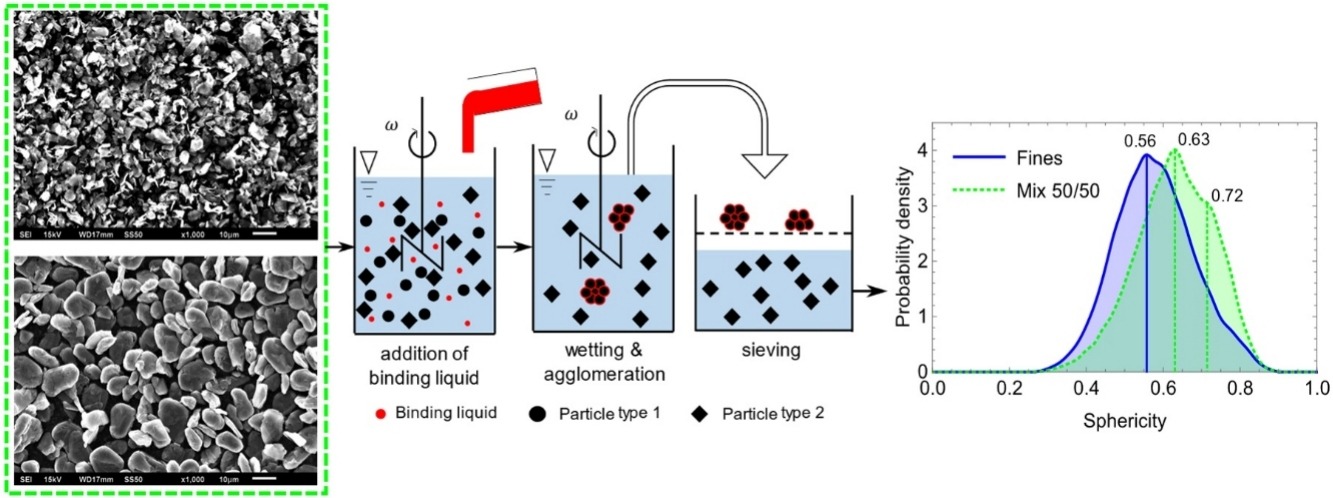
Objective of this work was to develop a novel method for characterizing real 3D shapes of particles smaller than 20 μm by X-ray microtomography (X-RMT). Multidimensional separation of heterogenous solids through agglomeration in suspension will improve recycling processes as the particle shape and the agglomerate size are used for shape-selective separation. In the present paper we discuss the fundamentals of X-ray tomography and the experimental setup for selective spherical agglomeration in suspension. A specific preparation method of the particulate sample for X-RMT followed by 3D image processing, are essential for the shape analysis expressed as sphericity. We also discuss the limitation of this method due to the so-called Partial Volume Effect and particle clusters in the order of magnitude of X-RMT resolution. As proof of concept, we used a mixture of graphite platelets and spheronized graphite particles for a shape selective-agglomeration in suspension. The remaining fines were analyzed and showed more platelets than in the mixture. This indicates that spheronized particles are preferably bound in the agglomerates. These findings show that, based on the discussed sample preparation and a 3D image analysis in connection with X-RMT, particle shapes of micronized particles can be discriminated.