- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
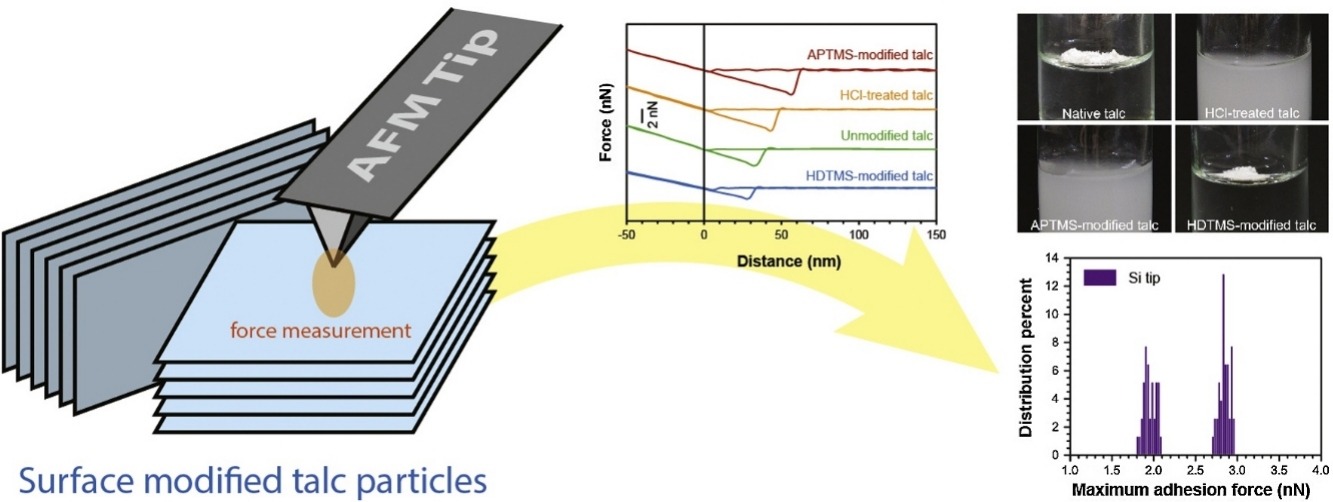
• From AFM measurement, adhesion of talc was found to result from van der Waals interactions.
• Anisotropic characters of talc surfaces persist even after surface modifications.
• Difference in hydrophobicity of different talc surfaces was experimentally verified.
As a versatile mineral, the crystalline hydrated magnesium silicate talcum, or talc, has been widely used in numerous industries from pharmaceutical formulations to composite material designs. Its efficient application as filler/additives incorporates the improvement in concomitant properties within materials, e.g., strength, which involves interactions between talc particles and aqueous/nonaqueous matrices. Successful property enhancement imposes ideal mixing and homogenous adhesion within a talc particle, but they are limited by the coexistence of face and edge surfaces of talc, which exhibit different level of hydrophobicity. Here, using atomic force microscopy force spectroscopy, we showed that although hydrophilic talc particles obtained from acid treatment or aminosilanization better adhered with materials representing a matrix, the anisotropic characters of the two surface types persisted. Conversely, the degree of talc’s surface anisotropy reduced with the surface hydrophobization by aliphatic methylsilanization, but followed by the decrease in adhesion. With ten-fold difference in Hamaker constants of the probe/talc surface interacting pairs, we showed that the adhesions resulted from van der Waals interactions that suggested the influence of surface polarity. The insight from this work would provide grounds for strategies to modulate talc’s adhesion, hydrophobicity and surface uniformity.