- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
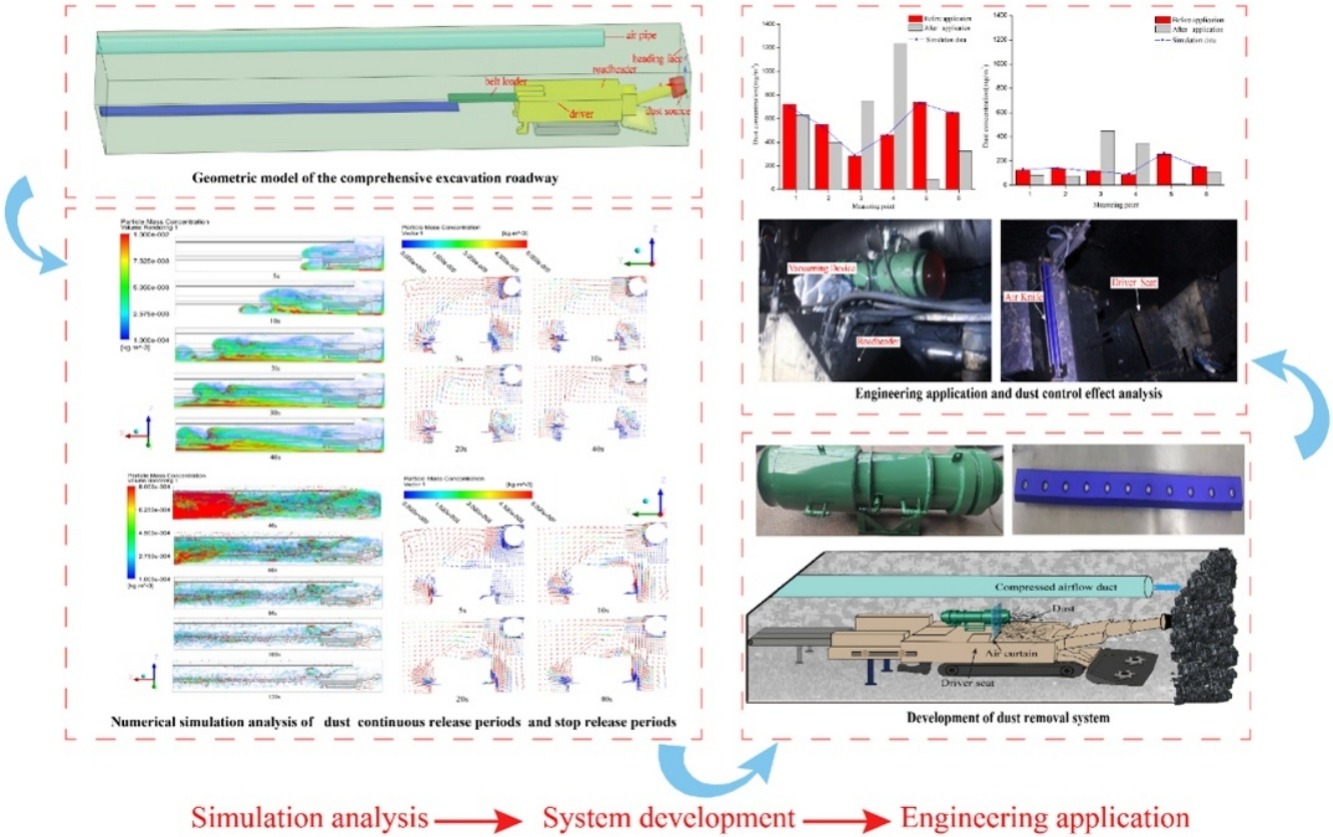
• Dust dispersion characteristics during CRP and SRP were simulated respectively.
• Dust distributions and migration actions around road-header drivers have been analyzed.
• Dust separation and extraction systems used for driver protection was developed.
• Effect of dust removal before and after application of the systems was analyzed.
In the present study, a numerical simulation method was adopted in order to examine the characteristics of dust dispersion during continuous dust release periods (CRP) and stop dust release periods (SRP). The purpose was to analyze the dust distributions and migration actions around road-header drivers in excavation roadways, and then determine effective dust control measures for underground coal mines. This study’s simulation results showed that the dust concentrations continuously increased, and then gradually reached a stability level during the CRP. During that time, the locations of the drivers were always at the intersection of the original migration dust and the backflow dust, and the drivers were invaded by these two strands dust. However, during the SRP, the dust concentrations gradually decreased under the actions of the roadway ventilation. Besides, obvious backflow phenomena were observed around the road-header during the SRP. The locations of the drivers were still within the backflow paths of the high dust concentrations. At the present time, dust separation and extraction systems have been implemented in coal mines, including vacuuming and air knife devices, which are designed to control the dust around the road-header drivers. The field applications of these systems were conducted in the 26 mechanized excavation faces of the Zhangcun Coal Mine. The results revealed that the use of these dust removal systems could effectively reduce the dust concentrations around the road-header drivers. In the present study, the dust removal rates during the CRP and SRP were determined to reach up to 88.7% and 94.6%, respectively. Therefore, the results of this research study provided effective theoretical guidance of the characteristics of dust distributions in coal mines, and introduced effective control methods for the hazardous dust concentrations around road-header drivers during the excavation process.