- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
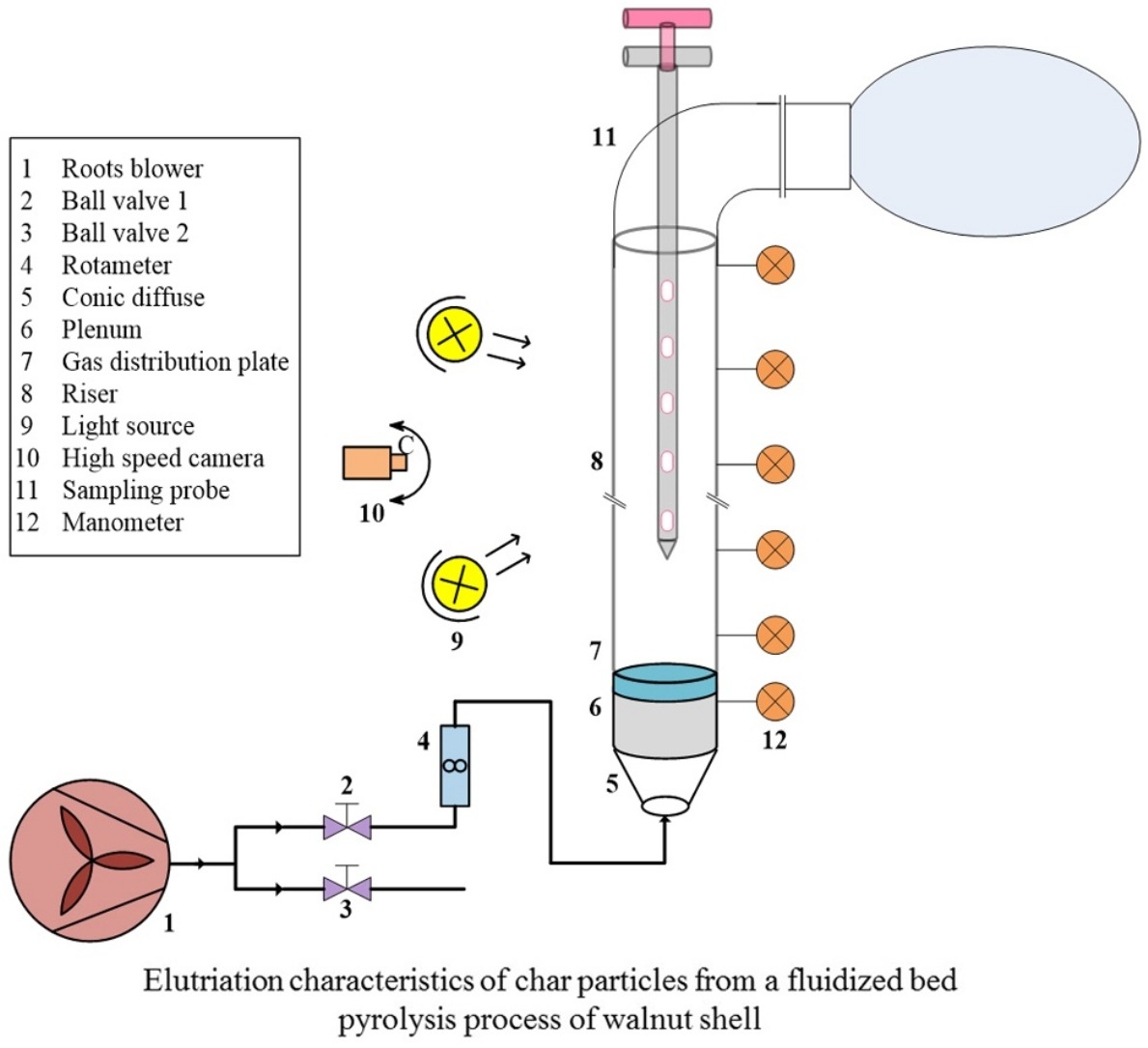
• Effect of gas velocity and composition of multi-component mixtures on elutriation.
• Mechanisms of particle entrainment are proposed.
• Particle concentration distributions of multi-component mixtures are reported.
• Transport disengagement and elutriation rate of fluidized bed mixtures are discussed.
• Method for gas velocity optimization is proposed.
Multi-component mixtures were prepared to simulate a bed of walnut shells undergoing pyrolysis in acold fluidized bed. Four mixtures with different ratios of walnut shell, semi-chars, and clean char were used. Batch elutriation experiments using these mixtures were performed in a transparent fluidized bed to allow direct observation of the flow patterns and particle composition. The results indicated that the bubble wake rather than bubble nose was primarily responsible for particle entrainment at higher gas velocities, and that coarser particles would be “transformed” into elutriable particles. Dimensionless gas velocities ranged from 0.2 to 1.0 and an exponential decrease in particle concentration with respect to bed height was observed. The transport disengagement height (TDH) gradually increased with the gas velocity until the entire bed layer enters a pneumatic transport state. Notably, larger TDHs were required when the bed contained a larger fraction of light components. Two characteristic parameters were used to evaluate particle elutriation: the elutriation rate constant (K), and the residual volatile content of the elutriated particles (v′). These parameters were used to optimize operating gas velocity for the fluidized bed.