- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
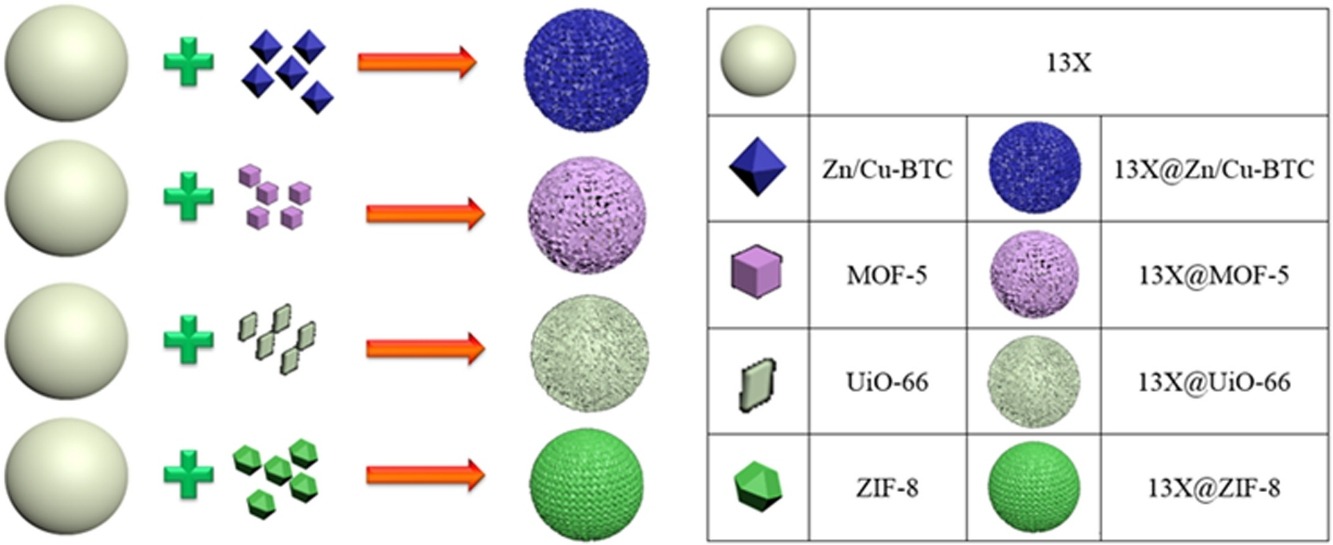
• A novel millimeter-scale 13X@MOF composite was designed and fabricated.
• 13X@UIO-66 notably exhibited excellent stability immersed in water, strong acidic, and basic aqueous media.
• OC capture abilities of 13X@UiO-66 only exhibited slight change after the fifth round.
Many metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) trapped in water exhibit instability and small-particle agglomeration issues, which unquestionably constrain their potential applications, such as the capture of organic contaminants (OCs). In this study, four types of micron-sized MOFs (Zn/Cu-BTC, MOF-5, ZIF-8, and UiO-66) were grown within a zeolite-13X support to form millimeter-sized zeolite-13X@MOF composites for the elimination of benzothiophene, methyl orange, and tetracycline from the liquid phase by dynamic adsorption in a column. We observed that the 13X@Zn/Cu-BTC exhibited extraordinarily high OC capture capacities as a result of the Zn2+ and Cu2+ combinative effects of the acid–base interaction. Remarkably, the 13X@UiO-66 preserved its structural integrity when immersed in water for 15 days, in contact with boiling water for 12 h, and in both strong acidic and basic aqueous media. Moreover, the OC capture abilities of the 13X@UiO-66 only underwent a slight change after the fifth round. This work provides new method for the design of desirable millimeter-sized zeolite@MOFs, thereby advancing their practical application for OC capture.