- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Integration of a dust source term in a DEM-CFD multiphase framework.
• Prediction of dust emissions from bulk material during particle–fluid interaction.
• Application: Modelling dust release from stockpiles and packed beds.
• Deriving of dust release correlations in a wide parameter study.
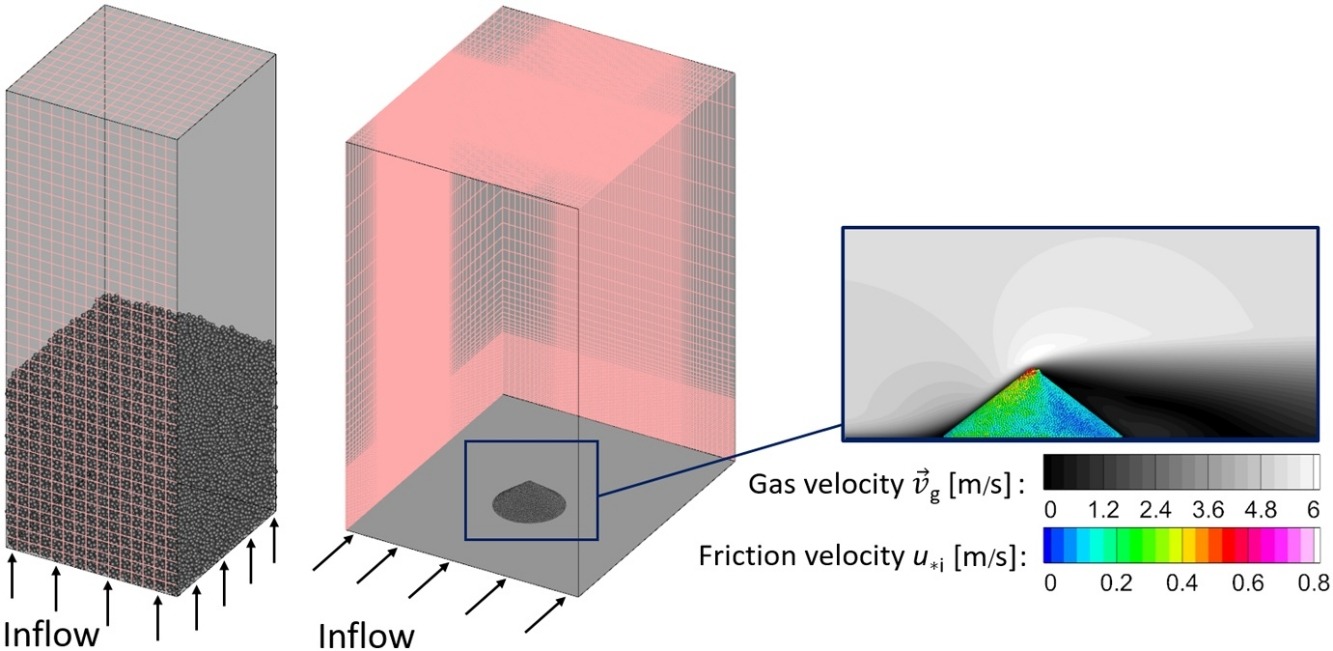
Dust emissions during storage of non-moving bulk materials are studied with a numerical method. The model relies on a contact-model-free Discrete Element Method (DEM) to model the bulk particle–fluid interaction and the dust removal coupled with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to model the gas and the dust phase in a multiphase framework. Here, two storage scenarios are considered: a flown through packed bed and a flown over stockpile. For the first, the performed simulations reveal that the dust discharge can be correlated with the passing fluid pressure drop. For the second, a parameter study of factors influencing the dust emissions is performed. The parameters discussed are the stockpile size, the gas velocity, the slope angle, the particle diameter and the shape of the stockpile, taking into account conical and truncated conical stockpiles. Dust release correlations are obtained for both scenarios, which reflect very well the obtained numerical results.