- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
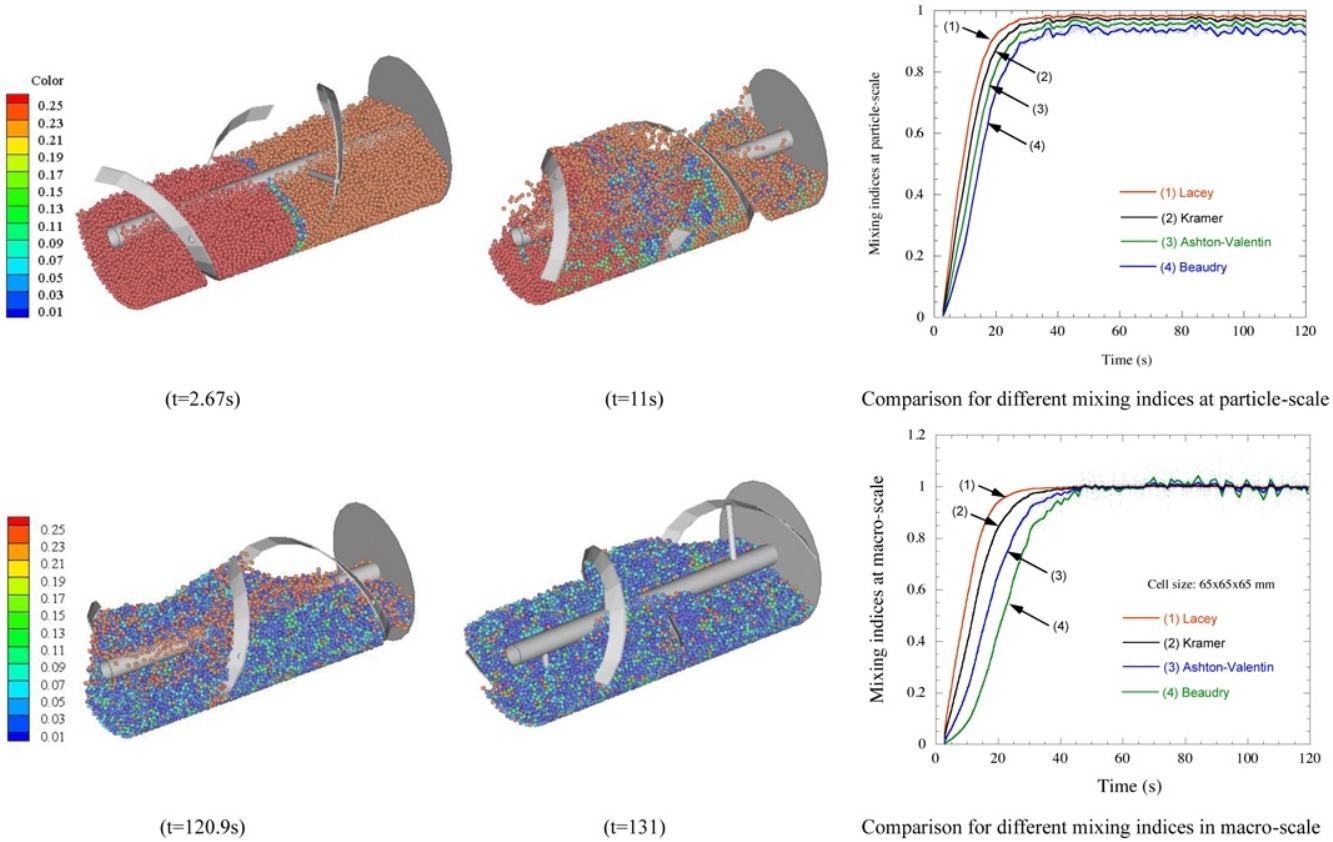
• The accuracy of mixing indices in a cylindrical ribbon mixer is studied by DEM.
• The results of several mixing indices are compared at particle scale and macro-scale.
• Non-sample variance methods are used to compare against the sample variance methods.
• Lacey index is the most suitable index among the indices considered in this study.
Mixing index is an important parameter to understand and assess the mixing state in various mixers including ribbon mixers, the typical food processing devices. Many mixing indices based on either sample variance methods or non-sample variance methods have been proposed and used in the past, however, they were not well compared in the literature to evaluate their accuracy of assessing the final mixing state. In this study, discrete element method (DEM) modelling is used to investigate and compare the accuracy of these mixing indices for mixing of uniform particles in a horizontal cylindrical ribbon mixer. The sample variance methods for mixing indices are first compared both at particle- and macro-scale levels. In addition, non-sample variance methods, namely entropy and non-sampling indices are compared against the results from the sample variance methods. The simulation results indicate that, among the indices considered in this study, Lacey index shows the most accurate results. The Lacey index is regarded to be the most suitable mixing index to evaluate the steady-state mixing state of the ribbon mixer in the real-time (or without stopping the impeller) at both the particle- and macro-scale levels. The study is useful for the selection of a proper mixing index for a specific mixture in a given mixer.