- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• A SuperDEM solver was developed for non-spherical particulate systems.
• A contact algorithm with accelerating and stabilizing strategy was developed.
• A particle-arbitrary wall contact algorithm using an STL method was developed.
• SuperDEM was validated in different particulate systems.
• Solver was MPI parallelled and100 million particles were simulated on 6800 cores.
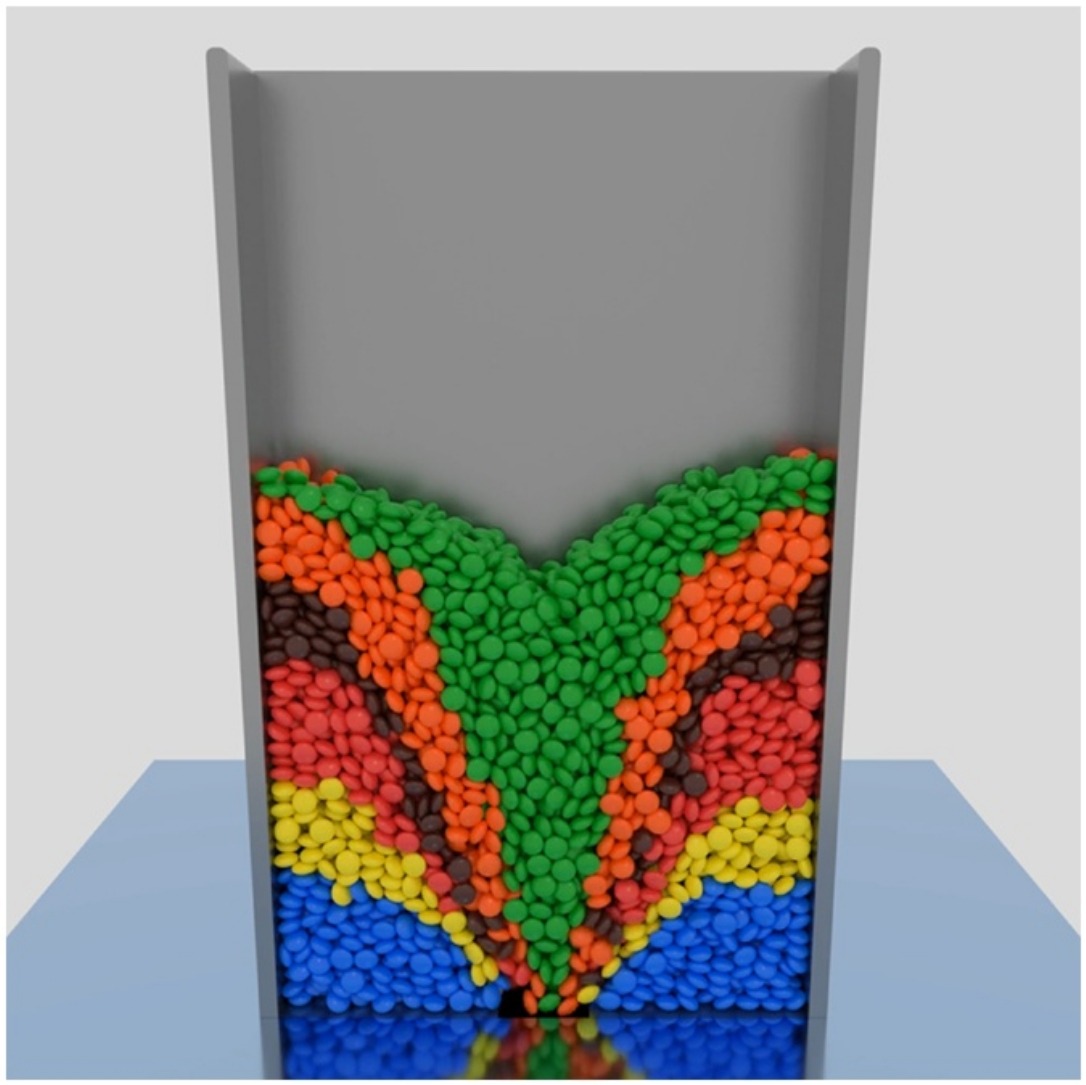
This article presents the development and validation of the Superquadric Discrete Element Method (SuperDEM) for non-spherical particle simulation using a superquadric particle method in open-source CFD suite MFiX. A superquadric particle–particle contact algorithm with accelerating and stabilizing strategy was developed. A superquadric particle–arbitrary wall contact algorithm was developed, which enables the simulation in complex geometry. The solver was validated by comparing with experimental data generated in this study or available in the literature. Tests include cylinder contacting with a wall, static packing of M&M chocolate candies in a cylindrical container, static packing of cylinders in a cylindrical container, dynamic angle of repose of cylinders in a rotating drum, and discharging of chocolate candies from a hopper. Besides, MPI parallelization of the solver was implemented and the parallel performance of the solver using MPI was assessed through large-scale simulations of 1 million, 10 million, and 100 million particles on up to 6800 cores, which demonstrates that the SuperDEM solver has great potential for industrial-scale systems simulation.