- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Fluid forces on spherical particles attached to a large-scale wall roughness structure.
• High-resolution Lattice–Boltzmann simulation with local grid refinement.
• Model roughness made of homogeneously distributed rows of semi-cylinders.
• Drag and lift strongly depends on the geometry of asperity structure.
• Estimation of detachment probability showed sliding is mostly occurring.
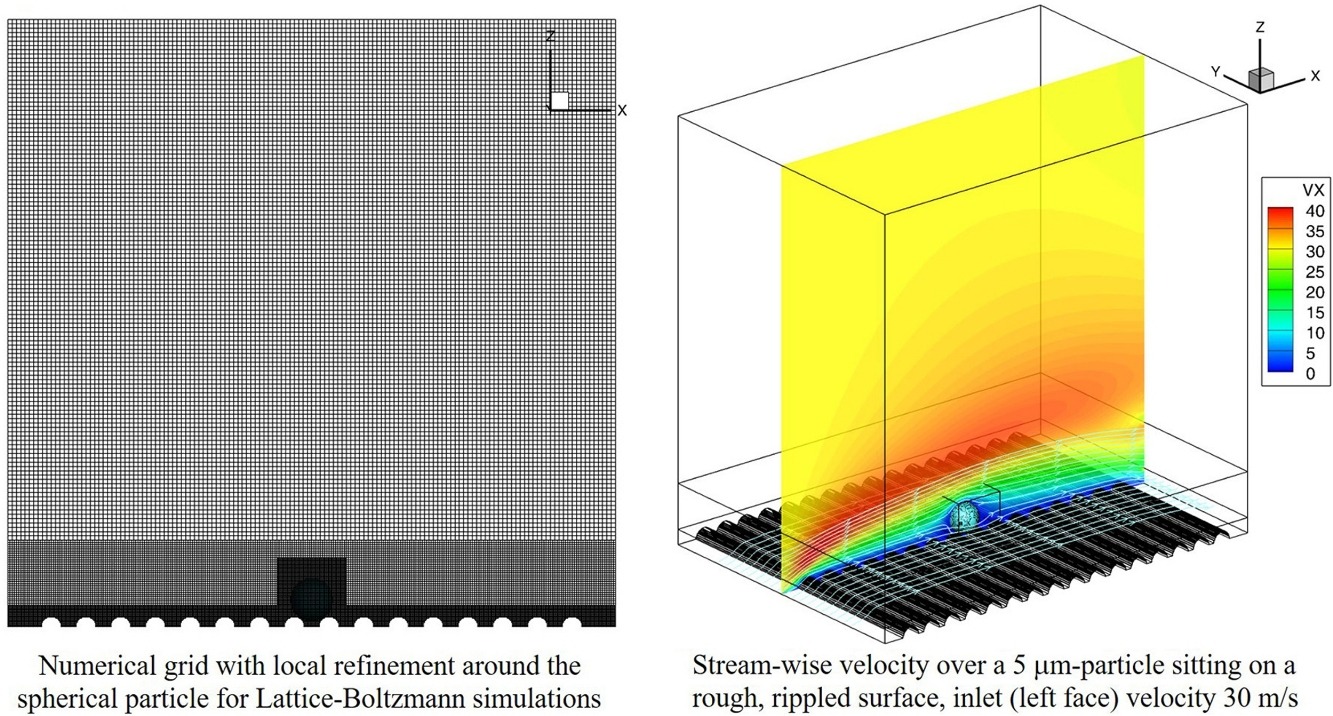
Fully resolved numerical simulations of a micron-sized spherical particle residing on a surface with large-scale roughness are performed by using the Lattice–Boltzmann method. The aim is to investigate the influence of surface roughness on the detachment of fine drug particles from larger carrier particles for transporting fine drug particles in a DPI (dry powder inhaler). Often the carrier surface is modified by mechanical treatments for modifying the surface roughness in order to reduce the adhesion force of drug particles. Therefore, drug particle removal from the carrier surface is equivalent to the detachment of a sphere from a rough plane surface. Here a sphere with a diameter of 5 μm at a particle Reynolds number of 1.0, 3.5 and 10 are considered. The surface roughness is described as regularly spaced semi-cylindrical asperities (with the axes oriented normal to the flow direction) on a smooth surface. The influence of asperity distance and size ratio (i.e. the radius of the semi-cylinder to the particle radius, Rc/Rd) on particle adhesion and detachment are studied. The asperity distance is varied in the range 1.2 < L/Rd < 2 and the semi-cylinder radius between 0.5 < Rc/Rd < 0.75. The required particle resolution and domain size are appropriately selected based on numerical studies, and a parametric analysis is performed to investigate the relationship between the contact distance (i.e. half the distance between the particle contact points on two neighbouring semi-cylinders), the asperity distance, the size ratio, and the height of the particle centroid from the plane wall. The drag, lift and torque acting on the spherical particle are measured for different particle Reynolds numbers, asperity distances and sizes or diameters. The detachment of particles from rough surfaces can occur through lift-off, sliding and rolling, and the corresponding detachment models are constructed for the case of rough surfaces. These studies will be the basis for developing Lagrangian detachment models that eventually should allow the optimisation of dry powder inhaler performance through computational fluid dynamics.