- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
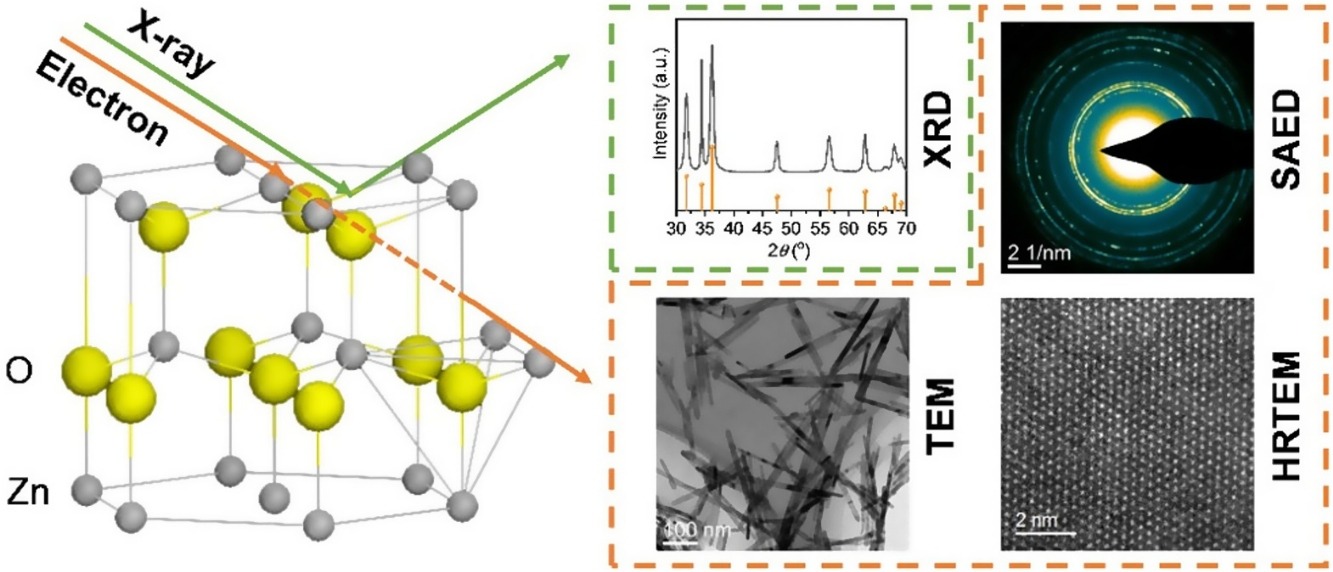
• Morphology and structure of ZnO were characterized and compared by XRD and TEM.
• SAED rings of ZnO with different morphologies are obviously different.
• Statistical analysis of SAED provides more accurate aspect ratio compared with XRD.
Nanomaterials with low-dimensional morphology display unique properties in catalysis and related fields, which are highly dependent on the structure and aspect ratio. Thus, accurate identification of the structure and morphology is the basis to correlate to the performance. However, the widely adopted techniques such as XRD is incapable to precise identify the aspect ratio of low-dimensional nanomaterials, not even to quantify the morphological uniformity with statistical deviation value. Herein, ZnO nanorod and nanosheet featured with one- and two-dimensional morphology were selected as model materials, which were prepared by the hydrothermal method and statistically characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results indicate that ZnO nanorods and nanosheets display rod-like and orthohexagnal morphology, which mainly encapsulated with {100} and {001} planes, respectively. The 7.36 ± 0.20 and 0.39 ± 0.02 aspect ratio (c/a) of ZnO nanorods and nanosheets could be obtained through the integration of the (100) and (002) diffraction rings in selected area electron diffraction (SAED). TEM combining with the SAED is favorable compare with XRD, which not only provides more accurate aspect ratio results with standard deviation values but also requires very small amounts of sample. This work is supposed to provide a convenient and accurate method for the characterization of nanomaterials with low-dimensional morphology through TEM.