- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
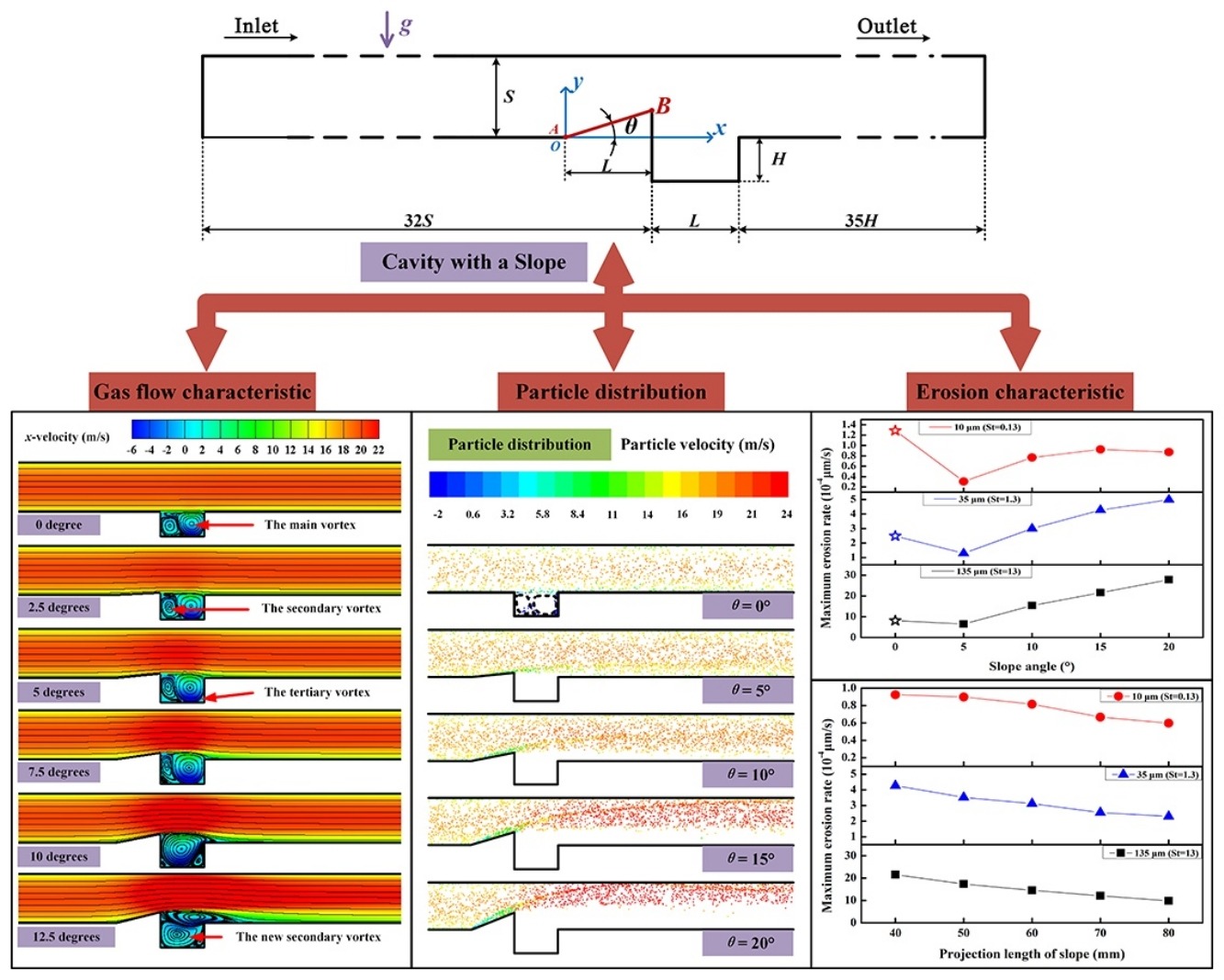
• A cavity with a slope in pneumatic conveying was investigated.
• Eulerian–Lagrangian method was used to study gas–solid flow.
• The slope has significant effect on gas flow and particle distributions.
• The slope can reduce the particles’ accumulation and the cavity’s erosion.
Gate valve is mainly used to turn on or turn off the pipeline in pneumatic conveying. When the gate valve is fully open, the particles are easy to collide with the cavity rear wall and enter into the cavity, resulting in particles’ accumulation in the cavity. The particles in cavity will accumulate between the cavity bottom and the flashboard bottom wall and prevent the gate from turning off normally. Meanwhile, the particles’ collision with cavity rear wall will cause serious erosion. Both the particles’ accumulation and erosion will cause the poor sealing of the gate valve, further resulting in the leakage of the pipeline system. To reduce the particles’ accumulation in cavity and erosion on cavity when the gate valve is fully open, we simplify the gate valve into a cavity structure and study it. We find that adding a slope upstream the cavity can effectively reduce the particles’ accumulation in the cavity and the erosion on the cavity rear wall. In this work, Eulerian–Lagrangian method in commercial code (FLUENT) was used to study the gas–solid two-phase flow and erosion characteristics of a cavity with a slope. The particle distribution shows that the particles with Stokes number St = 1.3 and St = 13 cannot enter the cavity due to the slope, but the particles with St = 0.13 enter the cavity following the gas. For St = 13, the particles collide with the wall many times in the ideal cavity. Erosion results show that the slope can transfer the erosion on cavity rear wall to the slope and reduce the maximum erosion rate of the wall near the cavity to some degrees.