- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
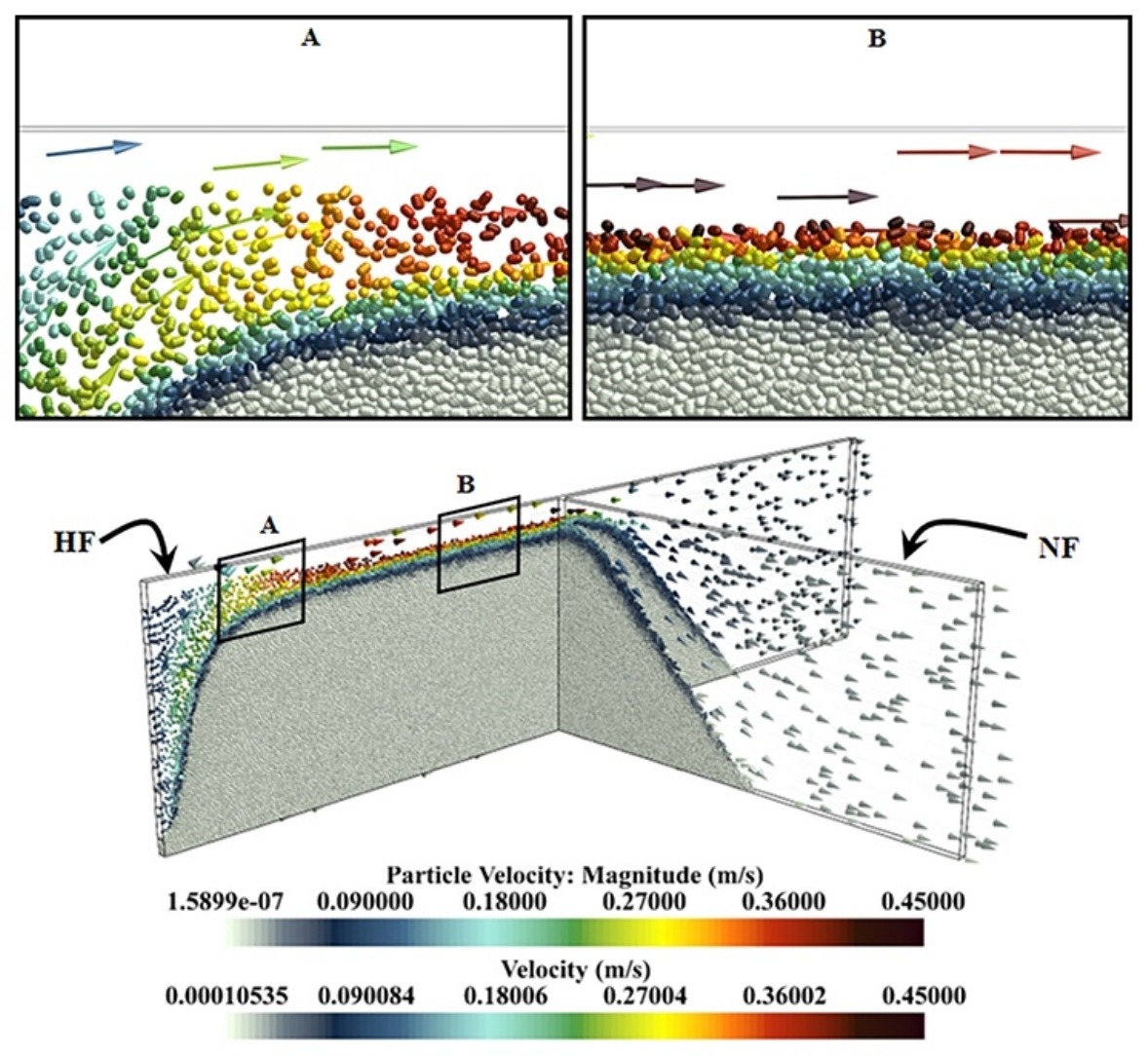
• Proppants-fluid flow in hydraulic and natural fracture intersection is simulated by CFD-DEM method.
• Sphericity effects are analyzed for different fluid inlet velocities and HF-NF intersection types.
• A new definition called blockage coefficient is introduced indicating severity and partiality of blockage.
• Effect of proppants concentration is negligible when proppants motion mechanism is bed load transport.
Proppants transport is an advanced technique to improve the hydraulic fracture phenomenon, in order to promote the versatility of gas/oil reservoirs. A numerical simulation of proppants transport at both hydraulic fracture (HF) and natural fracture (NF) intersection is performed to provide a better understanding of key factors which cause, or contribute to proppants transport in HF–NF intersection. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in association with discrete element method (DEM) is used to model the complex interactions between proppant particles, host fluid medium and fractured walls. The effect of non-spherical geometry of particles is considered in this model, using the multi-sphere method. All interaction forces between fluid flow and particles are considered in the computational model. Moreover, the interactions of particle–particle and particle–wall are taken into account via Hertz–Mindlin model. The results of the CFD-DEM simulations are compared to the experimental data. It is found that the CFD-DEM simulation is capable of predicting proppant transport and deposition quality at intersections which are in agreement with experimental data. The results indicate that the HF–NF intersection type, fluid velocity and NF aperture affect the quality of blockage occurrence, presenting a new index, called the blockage coefficient which indicates the severity of the blockage.