- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
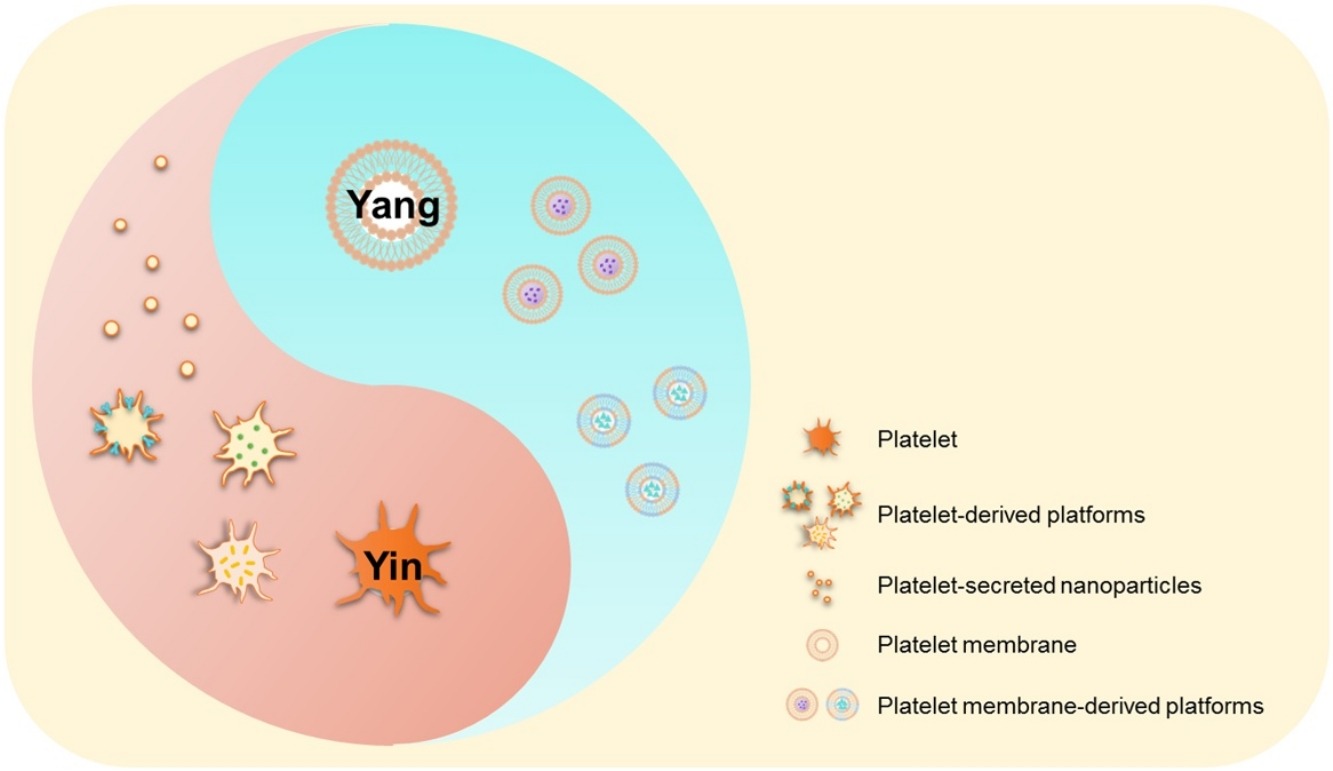
• Platelet-based biomimetic strategies have advantages over other anti-cancer therapies.
• Whole platelets and platelet membranes can circumvent host immune responses.
• These strategies provide enhanced tumor cell targeting and drug bioavailability.
• Cargos include apoptotic or photothermal agents or immune checkpoint inhibitors.
• Future directions for platelet-based biomimetic anti-cancer therapies are discussed.
Platelets contribute a major role in hemostasis by clumping and coagulation at the site of blood vessel injuries. In light of recent findings of a close relationship between platelets and immunological response, as well as interactions between platelets and cancer cells, novel engineering strategies have emerged for the integration of platelets or platelet membrane (PM) with anti-cancer therapeutics. In this review, we discuss several recent innovations that use platelets or their membranes to circumvent host immune responses and target tumor cells with high specificity to deliver a range of pharmacological, photothermal, or immunologic agents for eradication of recalcitrant tumor cells. More specifically, we compare the relative advantages of using whole platelets versus single or hybrid PM to coat nanoparticle cargoes. These cargoes range from well-established anti-tumor apoptosis-inducing agents, to relatively new photothermal agents that can induce a feedback cascade in which they induce vascular damage to the tumor which recruits more platelet- or membrane-encapsulated agents to induce further damage. We also discuss the use of engineered platelets to produce programmed cell death-inducing platelet derived microparticles. This review provides an overview and future directions for this promising platelet-based biomimetic approach to anti-cancer therapy.