- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
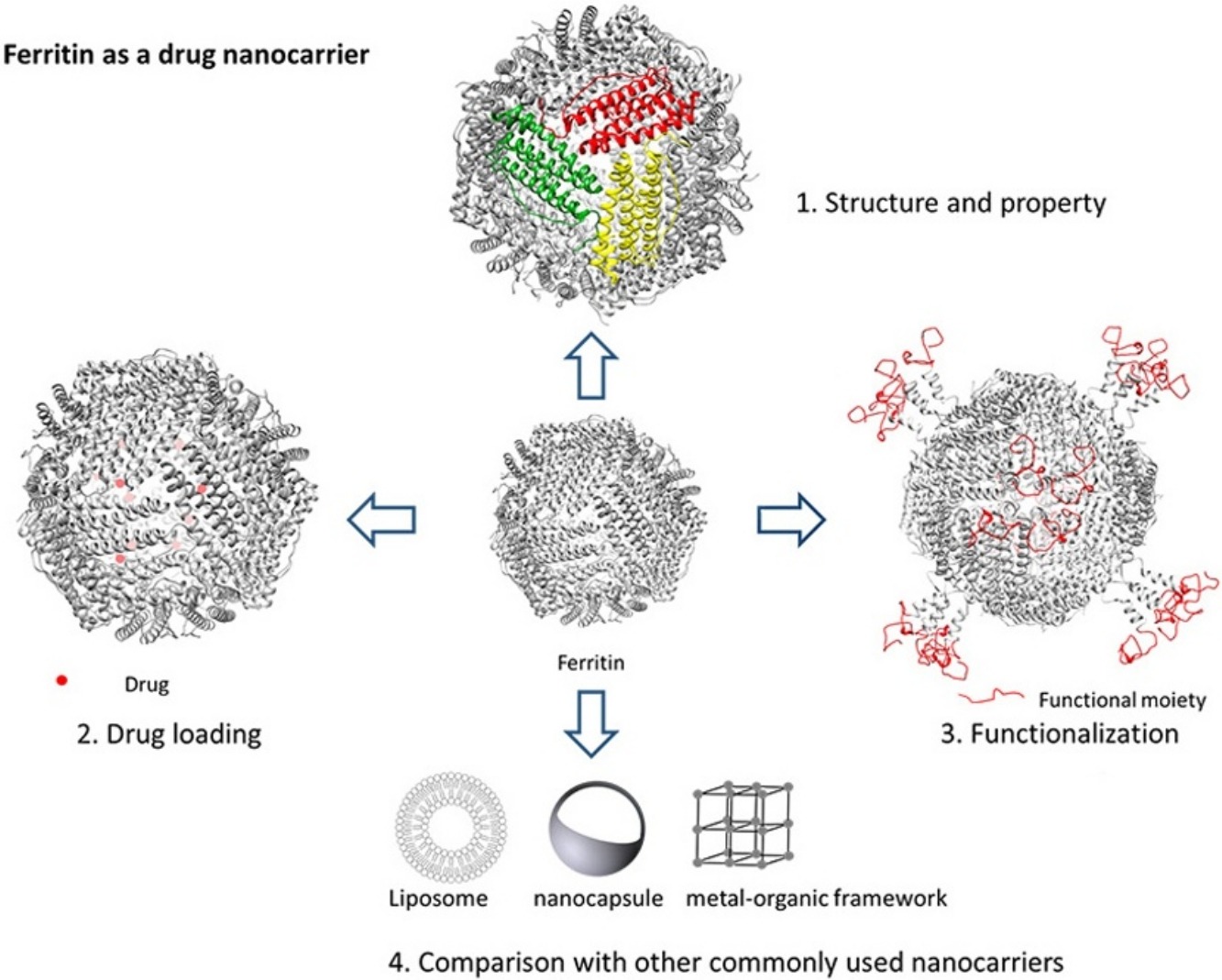
• Structure and properties afford solid foundation for ferritin as a drug nanocarrier.
• Drug loading approaches are diverse and applicable to different types of drugs.
• Functionalization of ferritin is by chemical conjugation, gene technology, hybridization.
• Drug loading performance and administration routes need improvement.
Ferritin stores and releases iron ions in mammals. It is globally important as a drug nanocarrier. This is because of its unique hollow-spherical structure, desirable stability and biological properties. Novel drug-loading approaches plus various functionalization approaches have been developed to improve ferritin in response to differing demands in disease treatments. Here, we critically review ferritin drug delivery and evaluate its diverse drug-loading and functionalization approaches, we: (1) Introduce basic structural and property information related to ferritin as a drug nanocarrier; (2) Contrast in detail the different means to load drugs and the selection of drug loading means; (3) Discuss multiple ferritin functionalization approaches, together with related advantages and potential risks; and, (4) Compare ferritin with alternative, commonly-used drug nanocarriers. We conclude that despite that no drugs based on ferritin are commercially available, the market potential for it is significant, and evaluate future research directions. Findings from this work will be of immediate benefit and interest to a wide range of researchers and manufacturers for drug delivery using ferritin.