- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
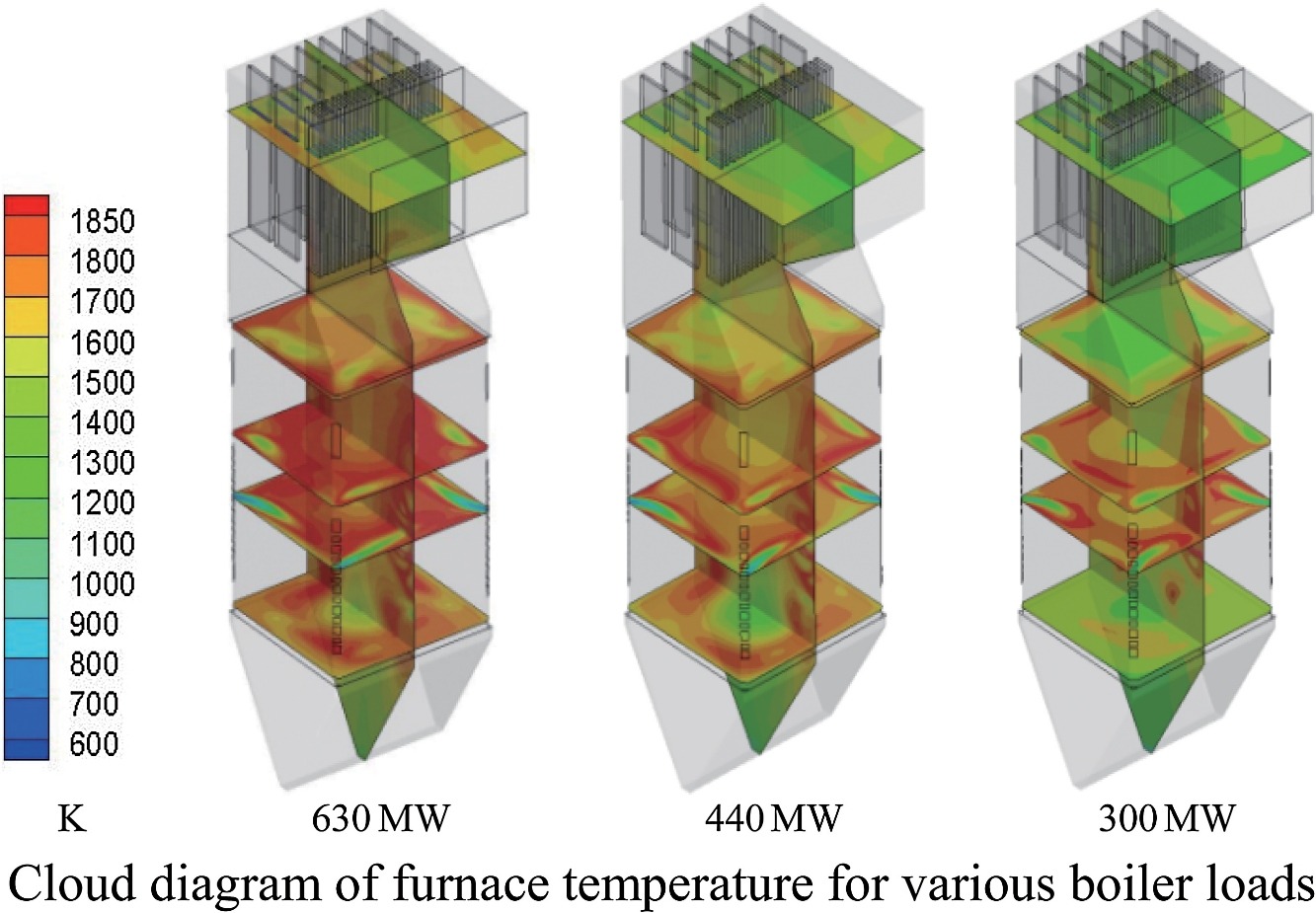
• Decreasing boiler loads impair air–fuel mixing and steady furnace combustion.
• High-temperature zone and flame move toward side walls with decreased boiler loads.
• O2 and NOx contents increase, whereas CO content decreases with reduced load.
• A decreased burner tilt angle favors heat transfer and NOx emissions.
This work presents a computational investigation of hydrodynamics, coal combustion and NOx emissions in a tangentially fired pulverized coal boiler at different loads (630, 440 and 300 MW; relative loads of 100%, 70% and 48%) to clarify the effect of load change on the furnace processes. A computational fluids dynamics model was established; the flow field, temperature profile, species concentration and NOx emissions were predicted numerically; and the influence of burner tilt angles was evaluated. Simulation results indicate that a decrease in boiler load decreases the gas velocity, attenuates the airflow rotations, and increases the tangent circle size. The high-temperature zone and flame moved toward the side walls. Such behaviors impair air–fuel mixing, heat transfer and steady combustion in the furnace. In terms of species concentrations, a decrease in boiler load increased the O2 content, decreased the CO content, and decreased the char burnout rates only slightly. A change in boiler load from 630 to 440 and 300 MW increased the NOx emissions from 202 to 234 and 247 mg/m3, respectively. Burner tilt angles are important in coal combustion and NOx emissions. A burner angle of –15° favors heat transfer and low NOx emissions (<185 mg/m3) for the current tangentially fired boiler.