- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
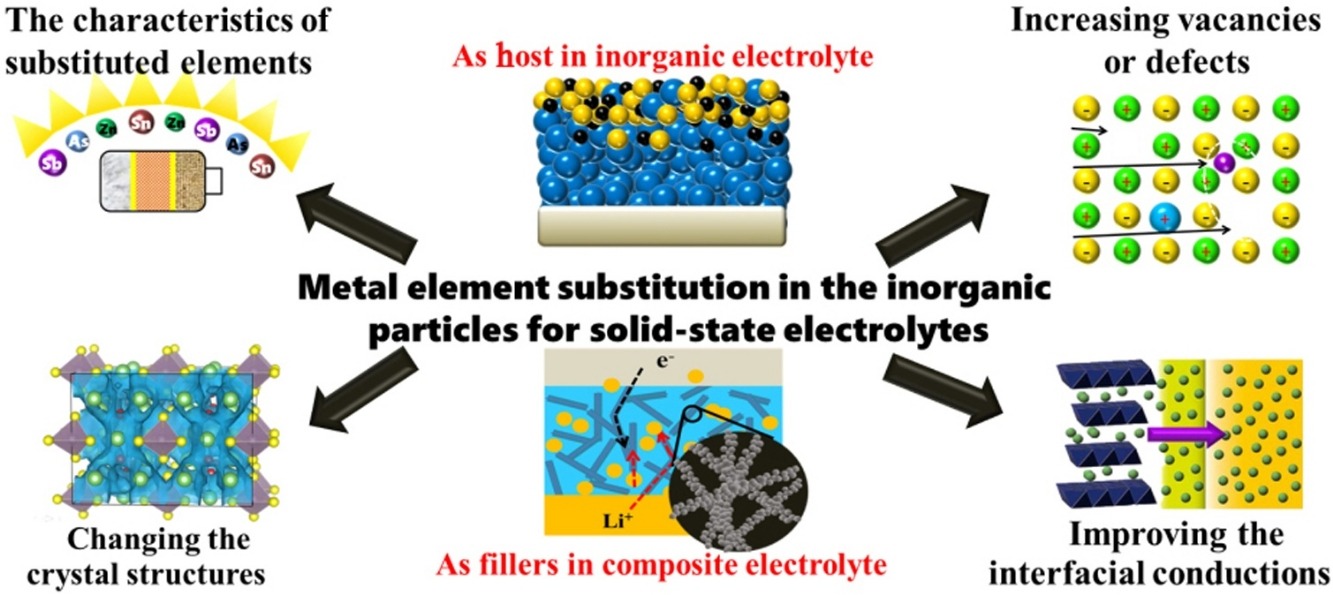
• Mechanisms of metal element substitutions in inorganic particles of solid-state electrolytes.
• Recent progress in bimetallic inorganic particles applied to lithium batteries.
• Metal element substituted strategies of inorganic particles in the field of solid-state electrochemistry.
All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs), receiving extensive attentions and studies, exhibit better safety, environmental friendliness, stability, wider electrochemical stability window and higher energy density than traditionally liquid lithium batteries. In a variety of inorganic materials, with highly replaceable, the non-lithium metal elements emerge in endlessly and affect performances in diversiform ways. Due to facile preparation, convertible structures and excellent properties, the lithium-containing bimetallic granular materials are often applied as important components of electrolytes in lithium batteries. In this review, in terms of the properties of substituted elements, changing crystal structures, increasing vacancies or defects and improving the interfacial conductions, the roles of metal element substitutions of inorganic particles on the improvement of solid-state electrolytes are expounded. And the applications of substituted strategies in ASSLBs as the host of inorganic particles electrolytes and as fillers or modifications for composite electrolytes are also investigated and discussed. It also summarizes the current concerns and obstacles that need to be broken through, as well as provides a basis guide for the selection and optimization of inorganic particles.