- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
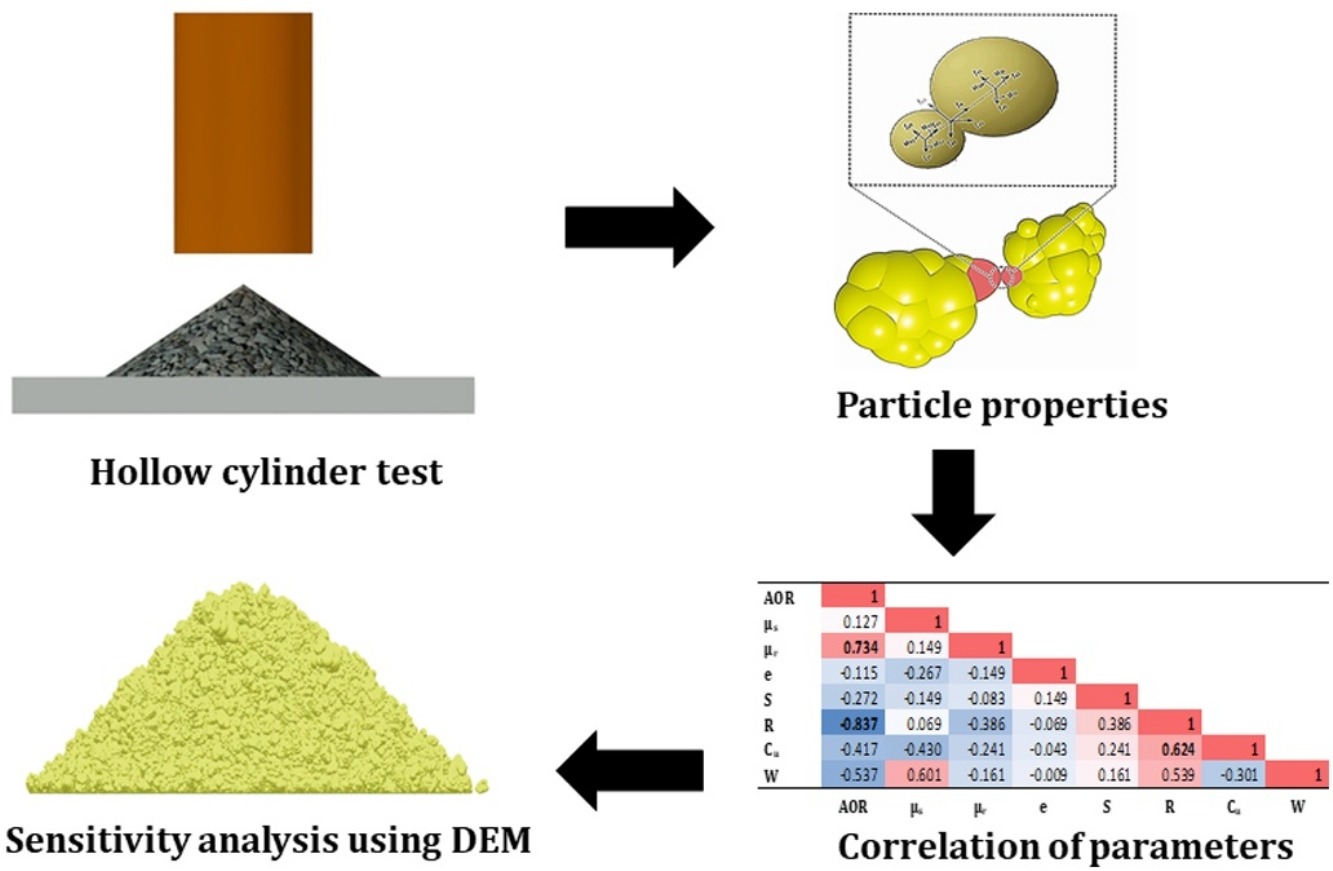
• Discrete element modeling of repose angle tests for ballast particles.
• Influence of particle properties on the repose angle of ballast samples.
• Estimation of ballast repose angle in terms of particles’ mechanical properties.
The discrete element method (DEM) is widely used in the realistic simulation of the shapes of particles. Researchers have considered the simplification of particle shapes owing to the high computational cost of such simulation. In this regard, the modeling of calibrated particles is a major challenge owing to the simultaneous effects of particle properties. The angle-of-repose test is a standard test method used to calibrate the bulk behavior of simulated particles. In the present study, the hollow-cylinder (slump) test was modeled for the verification of discrete element simulations. In this regard, a sensitivity analysis was conducted for all effective parameters, namely the static friction, rolling friction, restitution coefficient, sphericity, roundness, particle size distribution, and number of ballast particles. The results indicate that the rolling friction, roundness, number of particles, and size of particles are the most important parameters in the determination of the angle of repose (AOR). For particles in the range of ballast (20–60 mm), the effect of the number of particles on the angle of repose is reduced when the number is greater than 426. Additionally, it is concluded that angular particles can be replaced with sub-angular particles (R ≈ 0.2–0.45) with a higher rolling friction coefficient (μr > 0.14).