- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
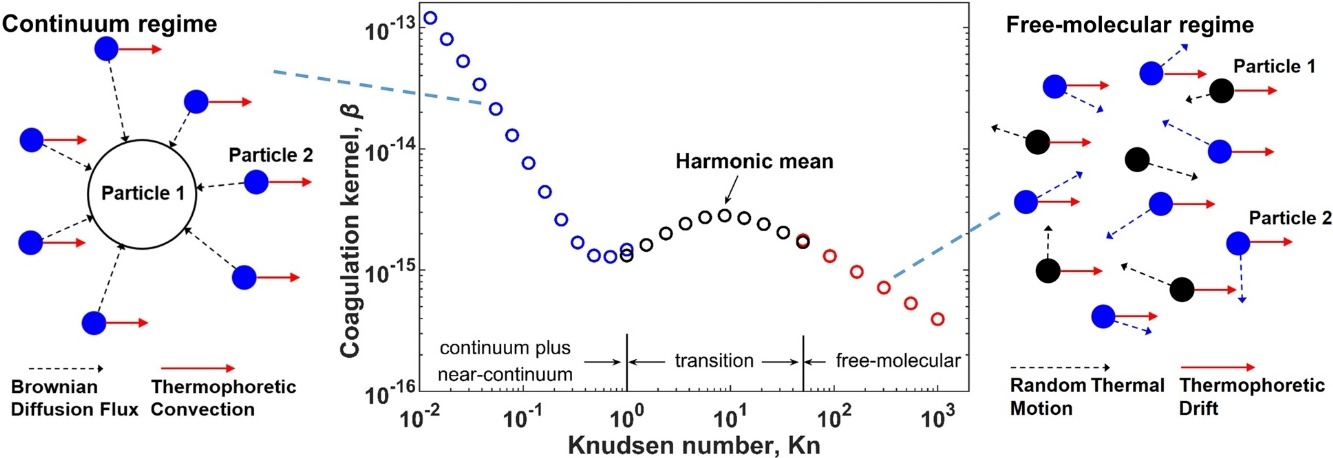
• Thermophoretically modified coagulation is presented for the entire size regime.
• Modified kernels are expressed as Brownian kernel times an enhancement factor.
• Enhancement effects are important in the continuum and transition regimes.
• Thermophoretic enhancement effects are ignorable in the free-molecular regime.
• Enhancement factor increases with decreased pressure, increased temperature and increased temperature gradient.
In many energy and combustion applications, particles experience large temperature gradients, which can affect the coagulation process due to thermophoresis. This study presents a rigorous theory of thermophoretically modified Brownian coagulation in the entire particle size regime. The theoretical derivations are based on the kinetic theory for the free-molecular regime and the harmonic mean method for the transition regime. The coagulation kernels in different size regimes can be expressed as the basic Brownian coagulation kernel times an enhancement factor. The enhancement factor represents the coagulation rate enhancement induced by thermophoresis and is a function of specific dimensionless numbers. Based on the enhancement factor, the thermophoretic enhancement effects on particle coagulation are further analyzed under a wide range of gas and particle conditions. The results show that thermophoretic enhancement effects are ignorable in the free-molecular regime, but need to be considered in the continuum regime and the transition regime. In addition, the enhancement effects increase significantly with increase of gas temperature and temperature gradient while decrease with increase of gas pressure. The present study can improve understanding of thermophoretic effects on Brownian coagulation in the entire size regime and provide a useful tool to calculate the coagulation rates in presence of thermophoresis.