- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
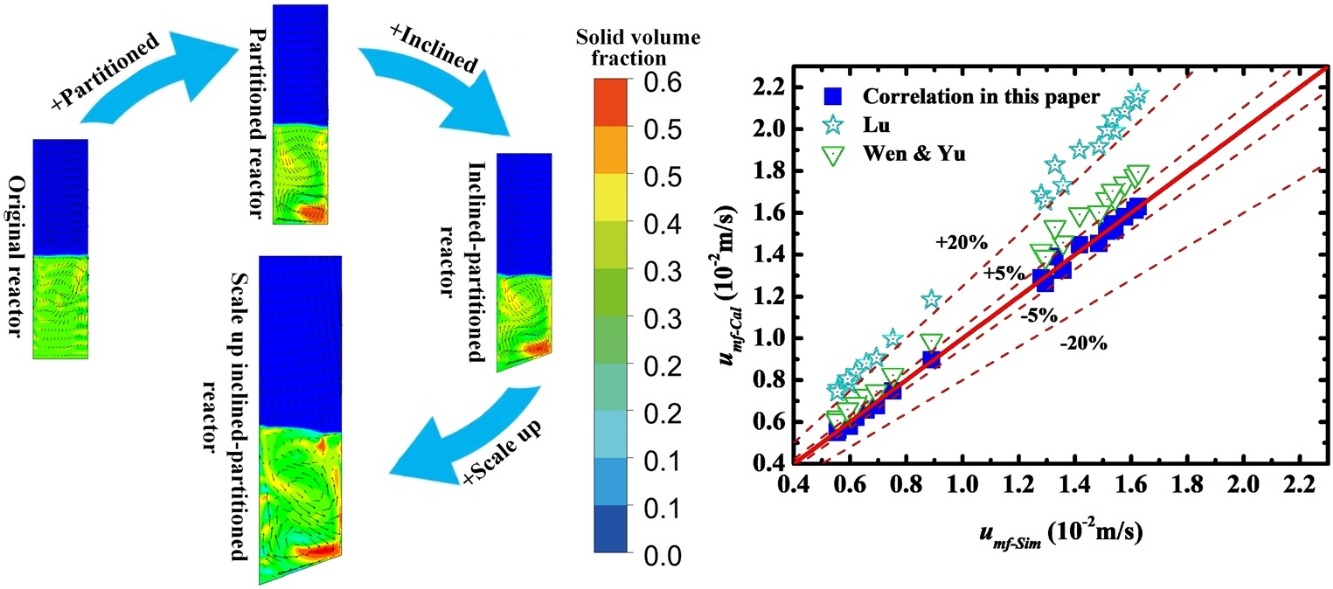
• Feasibility of using inclined distributor is examined in SCWFBR.
• An optimal inclined distributor structure is determined.
• Correlation for umf in optimal SCWFBR is established.
• A set of feasible rules for scaling up optimal SCWFBR is determined.
Supercritical water fluidized bed reactor (SCWFBR) is a novel concept for the gasification of coal and biomass to produce hydrogen. In this work, to enhance the mixing in the axial direction, an inclined distributor is introduced to optimize the flow dynamics in SCWFBR with partitioned fluid supply. Through numerical simulations based on the two fluid model (TFM), the effects of the inclined distributor structure and operating parameters on the solid distribution and the residence time are evaluated with the optimal values determined. Numerical results show that, area ratio = 2:1, SCW velocity ratio = 3:1, flow ratio = 3.36:1 and inclination angle = 20° are the optimal design in this paper. A predictive correlation of the minimum fluidization velocity for the improved SCWFBR is also proposed based on the numerical data. The average error between the correlation and numerical simulation results is approximately 1.4% which strongly demonstrates its capability. Finally, based on the optimal design, the lab-scale reactor is further scaled up and the studies about two scale-up rules are carried out. Only the cold flow is simulated in this study without considering chemical reaction which would be involved in future work.