- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
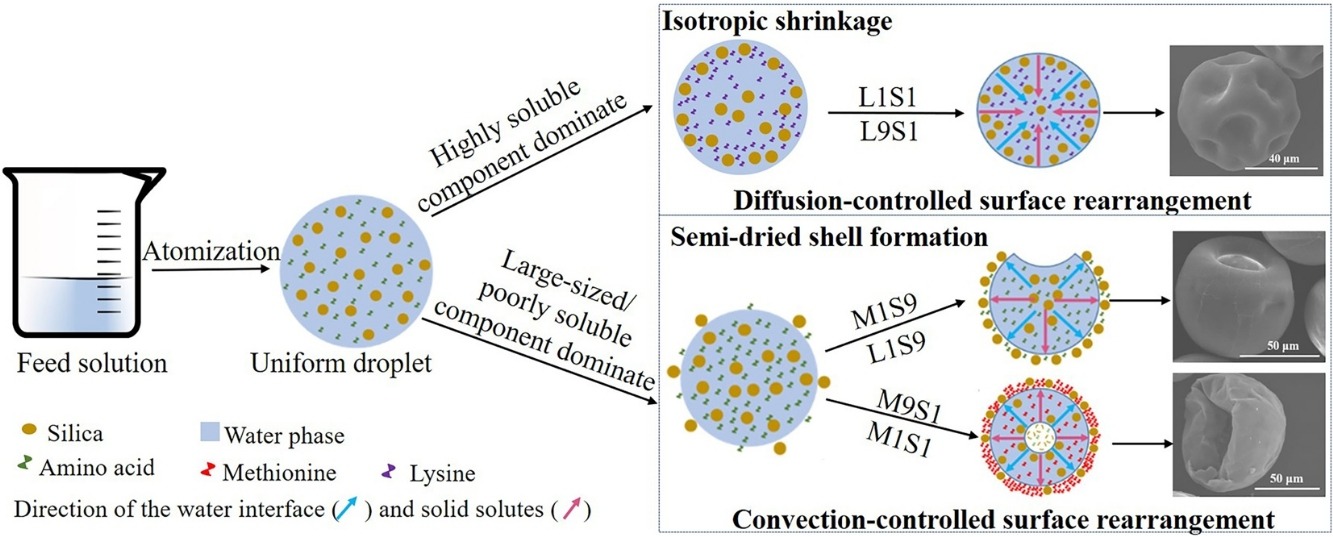
• Uniform two-component particles were fabricated via micro-fluidic spray drying.
• Component size and solubility were shown to have significant impact on surface composition.
• Construction of semi-dried shell was essential for mediating surface composition.
•“Convection/diffusion-controlled surface rearrangement” was proposed.
• Particle wettability was well correlated with respective surface composition.
This work is aimed to study the effects of component size and solubility on the surface composition of spray dried (SD) uniform two-component particles fabricated by micro-fluidic spray dryer. Various precursor liquid consisting of small molecular of methionine (Met, 33 g/L) or lysine (Lys, 739 g/L) and large-sized silica (12 nm) were prepared by adjusting the mass ratio of components. X-ray energy dispersive results showed that the respective enrichment degree (De) of Met and Lys on the surface of SD-M1S9 and -L1S9 prepared at 150 °C were 182 ± 9% and 125 ± 14%. The De of hydrophobic Met for SD-M1S1 and -M9S1 were 46 ± 9% and 4 ± 2%, respectively, whereas relative hydrophilic Lys mainly distributed internal of the particle meanwhile the De of silica on the surface for SD-L1S1 and -L9S1 were 17 ± 4% and 12 ± 1%, respectively. Drying temperature (120 and 180 °C) showed more apparent effect on the De of amino acid for the particles of less amino acid. The possible formation mechanism of surface composition and the surface composition impact on the wettability of particles were explored. These results provide new guidance for manufacturing functional SD powders with various components.