- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
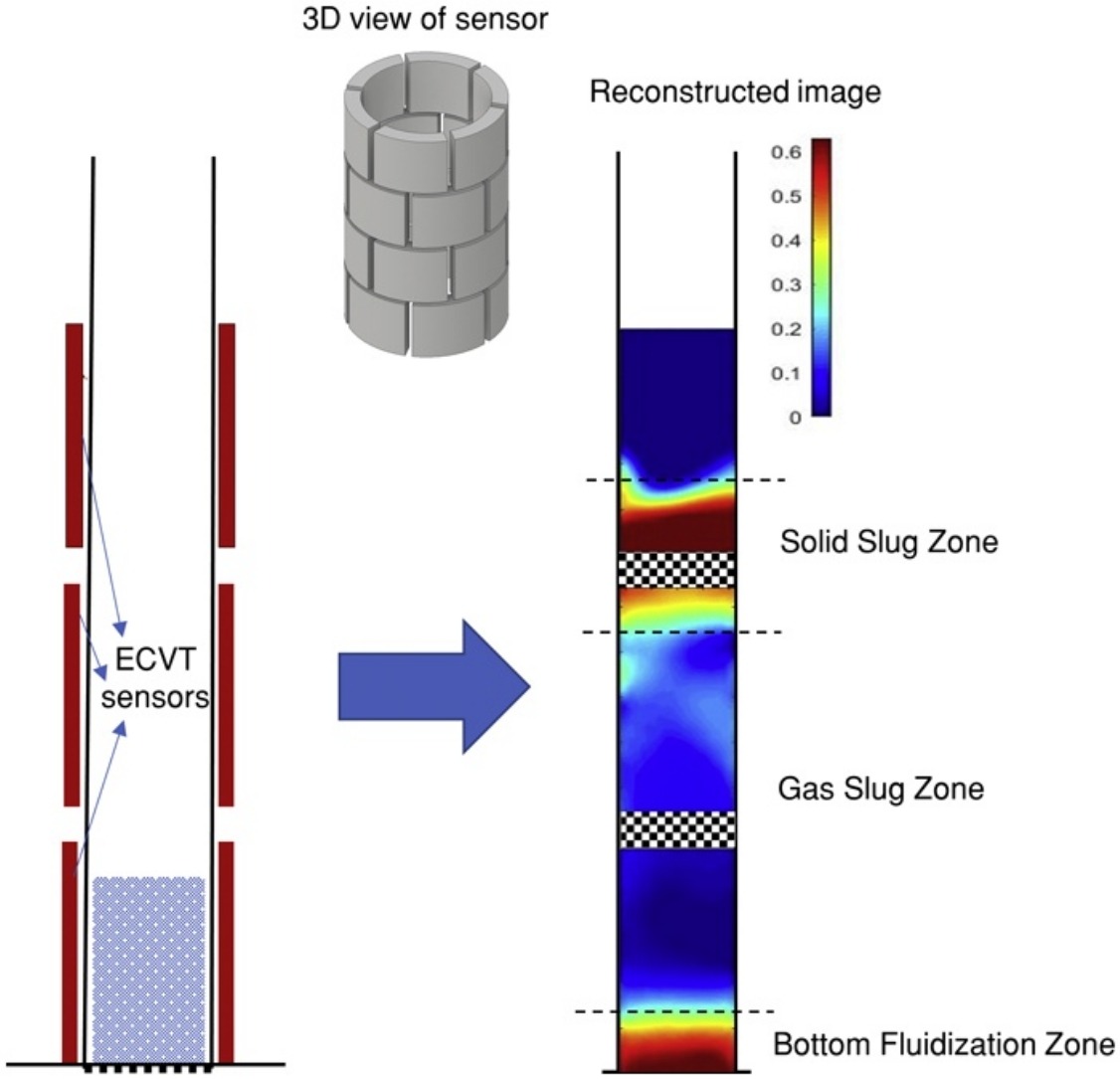
• Dynamic characteristics of square-nosed slugging are investigated using ECVT.
• Multiple ECVT sensors provided continuous, 3D imaging of the slugging bed flow.
• Three distinct zones are clearly observed during the evolution of the slug.
Slugging represents one of the major regimes in fluidization, which occurs in small diameter beds with large bed height-to-diameter ratio or in large diameter beds with internals that resemble multiple small diameter fluidized beds. Slug types include round-nosed slug, wall slug and square-nosed slug. Studies of the slugs have been mainly focused on round-nosed or wall slugs known as half slug, typically occurring in Geldart group A particle fluidization. The square-nosed slug typically occurring for Geldart group D particles appears to be regarded as simple in its structure. The Electrical Capacitance Volume Tomography (ECVT) imaging of the square-nosed slugging phenomena conducted in this study reveals otherwise. That is the structure of the square-nosed slug is, in fact, complex, particularly with respect to its dynamic variation in fluidization. More broadly, this study examines experimentally the hydrodynamic characteristics of the square-nosed fluidization regime. Specifically, simultaneous measurements from multiple ECVT sensors provide non-invasive, continuous, 3-dimensional imaging of the entire flow region of the slugging bed and hence enabling the dynamic characterization of the evolution of the slugs. The analysis of the 3D images reconstructed for real-time gas–solid volume fraction profile of the slugging fluidized bed indicates that there are three different zones, namely, the bottom fluidization zone, the gas slug zone, and the solid slug zone, co-existing in the bed. The three zones present different hydrodynamic characteristics during the slug evolution. It is found that varying the gas velocity of the slugging bed mainly varies the maximum length of the gas slug zone, while it only has a minor effect on the lengths of the bottom fluidization zone and solid slug zone. It also has an insignificant effect on the solid volume fraction of the three zones.