- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
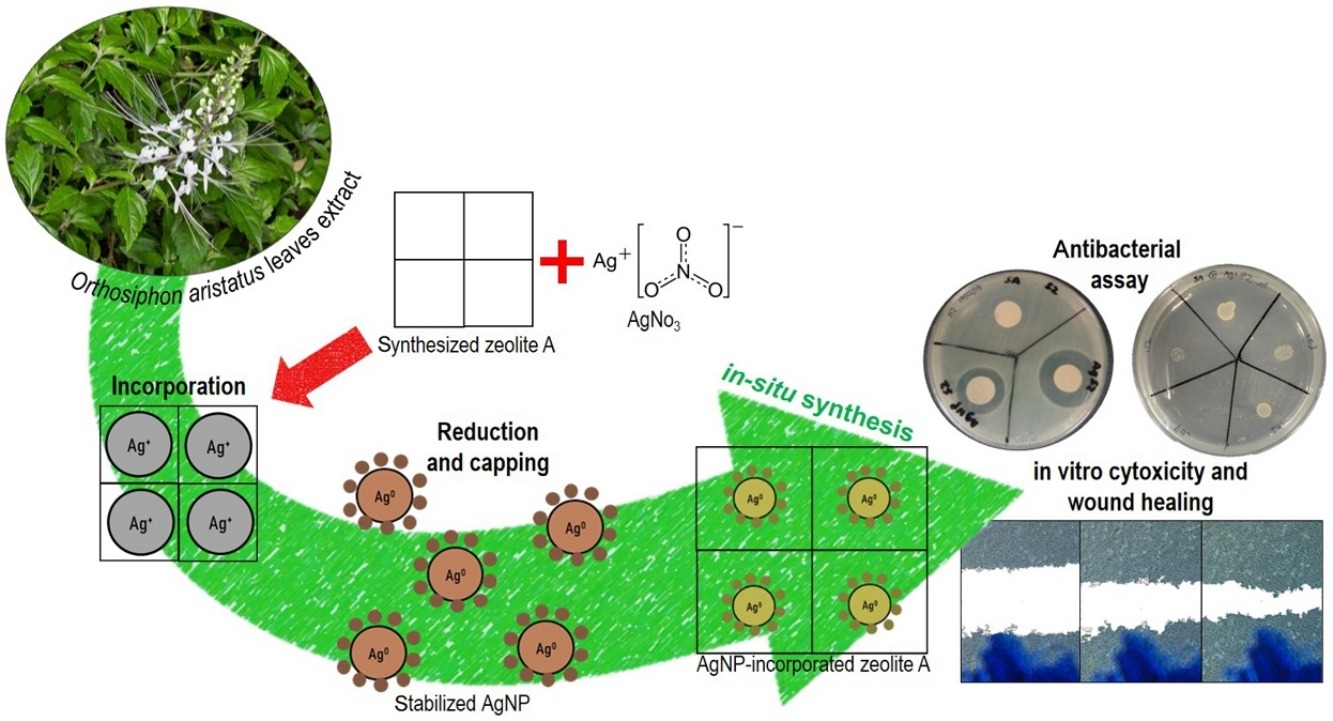
• Incorporation of silver nanoparticles into synthesized zeolite A framework.
• Orthosiphon aristatus leaves extract as a reducing agent for silver ions.
• Yield of bio-green AgNP incorporated on zeolite A through in situ synthesis method.
• Significant antibacterial activity of bio-green AgNP incorporated on zeolite A.
• No cytotoxicity and no hindrance in fibroblast wound healing.
The capability of synthesized zeolite A (SZ) to immobilize Ag ions (Ag-SZ) and Ag nanoparticles (AgNp-SZ) were comparatively studied. A novel approach of in situ biosynthesized AgNP-incorporated synthesized zeolite A (AgNp-SZ) was synthesized at an optimum volume of 0.4 mL of the Orthosiphon aristatus (O. aristatus) leaves plant extract (5%) using an in situ approach. In comparison, Ag-SZ was produced by loading the synthesized zeolite with Ag ions. All synthesized materials were characterized for their morphologies and physicochemical properties. The characterization analyses validate that the biosynthesized AgNP (<100 nm) using O. aristatus leaves extract was incorporated into the zeolite A. The antibacterial testing confirmed that these materials have antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli ATCC 11229 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538. MIC/MBC analysis demonstrated that in 0.9% saline solution, AgNP-SZ had higher antibacterial activity than Ag-SZ. The in vitro cell viability and migration assays were further examined towards human skin fibroblast cells HSF 1184. Results show that the materials are not cytotoxic to HSF 1184, and the biosynthesized AgNP-SZ promotes cell migration and proliferation higher than Ag-SZ. This research proved that the biocompatible antibacterial wound healing agent of AgNP-SZ can be synthesized using an in situ approach where the reduction process of Ag ions in the zeolite A can be performed using plant extract.