- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
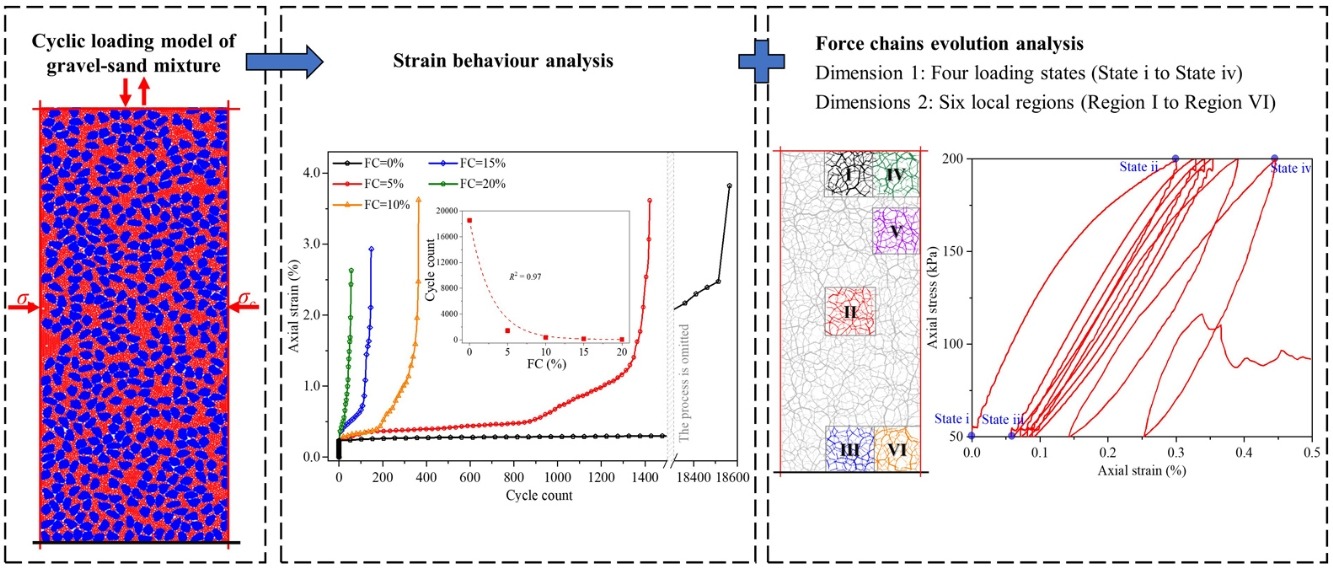
• Axial strain explains the logarithmic negative correlation between fines content and cycle count.
• Anisotropic characteristic of contact force under cyclic loading is described.
• Low fines content has no substantial influence on the evolution of force chain networks.
• Evolutions of strong and weak contacts are investigated from two dimensions: loading time and local space.
The strain characteristic and load transmission of mixed granular matter are different from those of homogeneous granular matter. Cyclic loading renders the mechanical behaviours of mixed granular matter more complex. To investigate the dynamic responses of gravel–sand mixtures, the discrete element method (DEM) was used to simulate the cyclic loading of gravel–sand mixtures with low fines contents. Macroscopically, the evolution of the axial strain and volumetric strain was investigated. Mesoscopically, the coordination number and contact force anisotropy were studied, and the evolution of strong and weak contacts was explored from two dimensions of loading time and local space. The simulation results show that increasing fines content can accelerate the development of the axial strain and volumetric strain but has little effect on the evolution of contact forces. Strong contacts tend to develop along the loading boundary, presenting the spatial difference. Weak contacts are firstly controlled by confining pressure and then controlled by axial stress, while strong contacts are mainly controlled by axial stress throughout the whole cyclic loading. Once compression failure occurs, the release of axial stress causes the reduction of strong contact proportion in all local regions. These findings are helpful to understand the dynamic responses of gravel–sand mixtures, especially in deformation behaviours and the Spatio-temporal evolution of contact forces.