- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
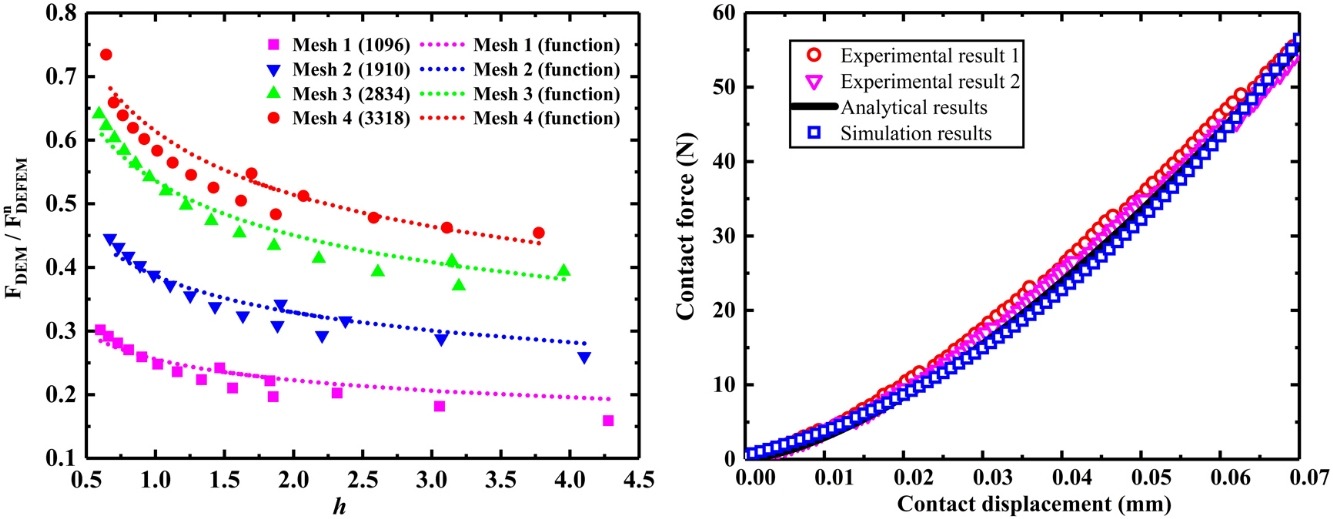
• Collisional surface is dynamically modeled by embedded discrete elements (EDEs).
• DEM is to solve external force and FEM is to solve internal force.
• Large deformation and motion of soft particle are solved by DEFEM separately.
• Computation of force and searching of contacts can also be treated by EDE.
• Packing of pebbles on rectangular and inclined walls are demonstrated by DEFEM.
The motion and deformation of soft particles are commonly encountered and important in many applications. A discrete element-embedded finite element model (DEFEM) is proposed to solve soft particle motion and deformation, which combines discrete element and finite element methods. The collisional surface of soft particles is covered by several dynamical embedded discrete elements (EDEs) to model the collisional external forces of the particles. The particle deformation, motion, and rotation are independent of each other in the DEFEM. The deformation and internal forces are simulated using the finite element model, whereas the particle rotation and motion calculations are based on the discrete element model. By inheriting the advantages of existing coupling methods, the contact force and contact search between soft particles are improved with the aid of the EDE. Soft particle packing is simulated using the DEFEM for two cases: particle accumulation along a rectangular straight wall and a wall with an inclined angle. The large particle deformation in the lower layers can be simulated using current methods, where the deformed particle shape is either irregular in the marginal region or nearly hexagonal in the tightly packed central region. This method can also be used to simulate the deformation, motion, and heat transfer of non-spherical soft particles.