- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
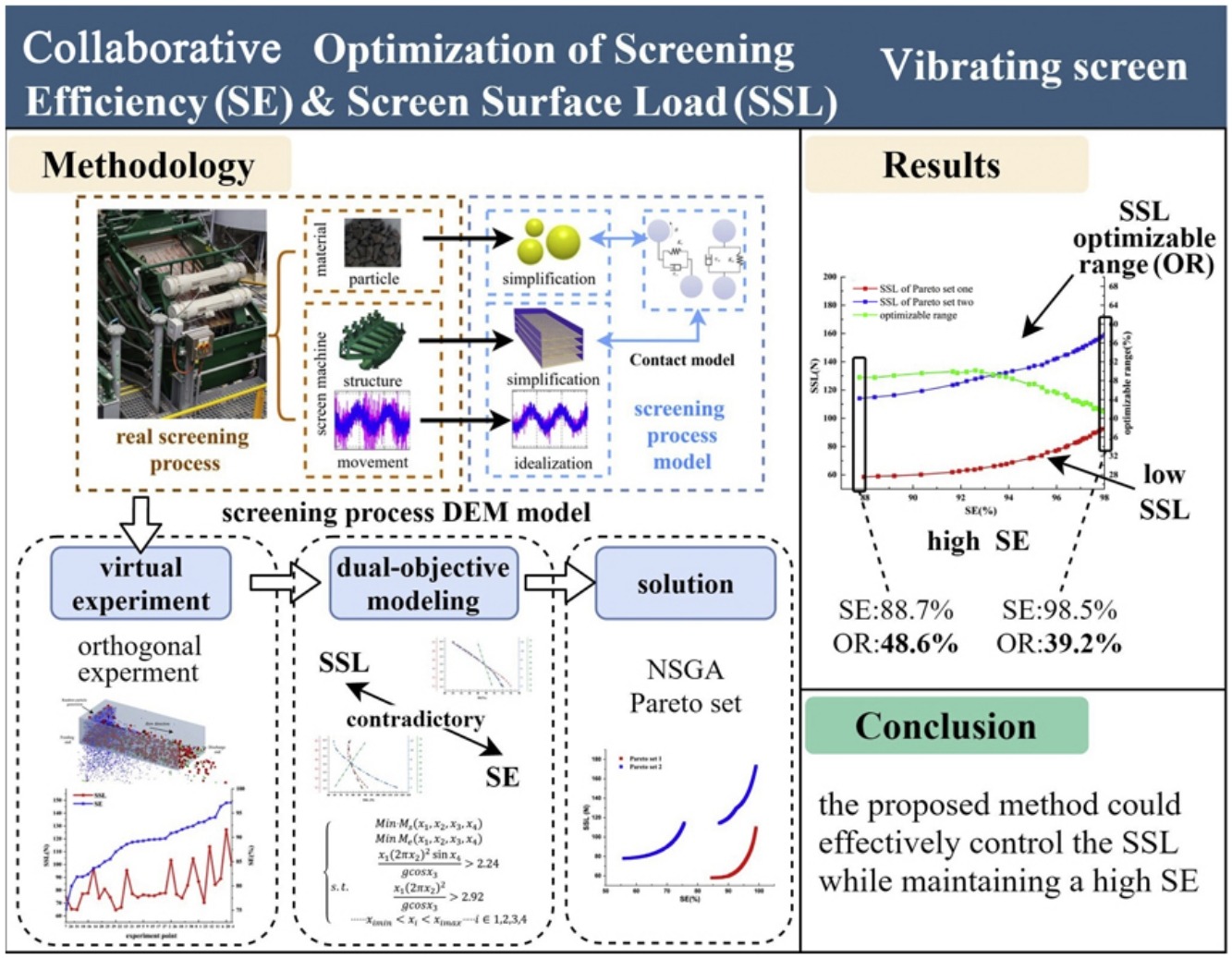
• Built the mathematical models of screening efficiency (SE) and screen surface load (SSL).
• Proposed a collaborative optimization method for SE and SSL.
• Optimized the SE and SSL for the linear vibrating screen.
The screen surface load (SSL) caused by granular materials is an important factor affecting the structural performance of vibrating screen. Based on virtual experiment, a multi-objective collaborative optimization method is proposed to control the SSL under high screening efficiency (SE) in this work. Firstly, a DEM model was established to study the influence of process parameters on SE and SSL. Secondly, the NSGA-II (Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm) was employed to optimize the screening parameters with both SE and SSL as targets. The optimization method proves to be effective implementing on a linear vibrating screening. With SE equals to 98.5%, the SSL optimizable range is 39.2%. While compromising the SE to 88.7%, the SSL optimizable range improves to 48.6%. The result shows that the collaborative optimization could effectively control the SSL while maintaining a high SE, which is of great significance to improve the service life of screen surface and screen body.